Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 33
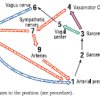
Baroreceptor Reflex Role Play
Source Institutions
In this activity about the baroreceptor reflex (BR) arc (page 123 of the PDF), learners discover the importance of maintaining adequate arterial blood pressure through a role playing exercise.
Building a Magic Carpet
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 89 of the PDF), learners compare and contrast pitch and roll motions by using a Magic Carpet maze similar to one that was used for Neurolab investigations about microgravity.

Measuring Your Breathing Frequency at Rest
Source Institutions
In this activity about the brain and sleep (on page 138 of the PDF), learners measure their resting breathing rates. Learners will discover that breathing frequencies vary amongst individuals.
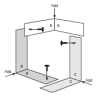
Building a 3-D Space Maze: Escher Staircase
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 95 of the PDF), learners create Escher Staircase models similar to those that were used by Neurolab's Spatial Orientation Team to investigate the processing of information about

Mirror, Mirror
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover that it is difficult to trace a curve by using its reflection in a mirror. Use this activity to discuss how the brain works.

Changing Body Positions: How Does the Circulatory System Adjust?
Source Institutions
In this activity about how the body regulates blood pressure (page 117 of the PDF), learners make and compare measurements of heart rate and blood pressure from three body positions: sitting, standing

Circles or Ovals?
Source Institutions
This science activity demonstrates the dominant eye phenomena. What does your brain do when it sees two images that conflict?

Shrinking Spot
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners control the (apparent) size of a hole with their brain.

The Braille Alphabet
Source Institutions
In this activity (8th activity on the page) about the sense of touch, learners make their own set of Braille letters. Learners use glue to make raised dots on a Braille Alphabet Sheet.

Seeing 3D
Source Institutions
Create 3D glasses and use them to explore color, light and optics. Fool your brain into 'seeing' three dimensions on a flat surface!
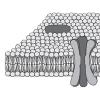
Build-A-Membrane
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners cut, fold, and paste paper representing biomolecules to create a three-dimensional cell membrane with embedded proteins.

Memory Solitaire
Source Institutions
In this online game, learners practice memory recall. They are shown a collage of pictures for two minutes, then have to write down everything they remember and check how they did.
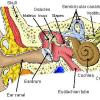
Model Eardrum
Source Institutions
In this activity (last activity on the page), learners make a model of the eardrum (also called the "tympanic membrane") and see how sound travels through the air.

Thaumatropes
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will make a thaumatrope, an old-fashioned optical illusion that dates back to the 1820s.

X-Ray Vision?
Source Institutions
In this activity (13th on the page), learners complete a simple illusion trick to see through their own hand.
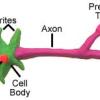
The Model Neuron
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create a model of a neuron by using colored clay or play dough. Learners use diagrams to build the model and then label the parts on a piece of paper.

Keep a "SLOG" (Sleep Log)
Source Institutions
In this activity (1st on the page), learners keep a "SLOG" or Sleep Log to study their sleep patterns.

Two Ears are Better Than One: Sound Localization
Source Institutions
This activity (9th activity on the page) about hearing demonstrates to learners the importance of having two ears.
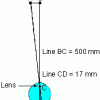
Measuring Your Blind Spot
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners calculate the width (horizontal diameter) of the blind spot on their retina. Learners make a blind spot tester using a piece of notebook paper.
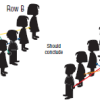
Target Recognition and Synapse Formation During Development
Source Institutions
In this activity about neuron/target muscle recognition (page 44 of the PDF), learners arranged in two rows facing away from each other use string to simulate neural development.
