Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 20

Altered Reality
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover that the human brain is highly adaptable. Learners try to toss beanbags at a target while wearing prism goggles.
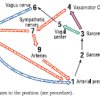
Baroreceptor Reflex Role Play
Source Institutions
In this activity about the baroreceptor reflex (BR) arc (page 123 of the PDF), learners discover the importance of maintaining adequate arterial blood pressure through a role playing exercise.

Pea Brain!: Explorations in Estimation
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use two different techniques to estimate how many little things fit into one bigger thing.

Drugs, Risks and the Nervous System
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners estimate risks associated with different events and compare their estimates to the real possibilities.
Building a Magic Carpet
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 89 of the PDF), learners compare and contrast pitch and roll motions by using a Magic Carpet maze similar to one that was used for Neurolab investigations about microgravity.

Pitch, Roll and Yaw: The Three Axes of Rotation
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 87 of the PDF), learners move their bodies to better understand the three axes of rotation: pitch, roll and yaw.

Measuring Your Breathing Frequency at Rest
Source Institutions
In this activity about the brain and sleep (on page 138 of the PDF), learners measure their resting breathing rates. Learners will discover that breathing frequencies vary amongst individuals.
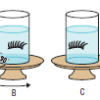
Visualizing How the Vestibular System Works
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 59 of the PDF), learners spin and observe false eyelashes in jars of water (prepared at least 1 day ahead of time) to investigate the effects of different types of motion on the
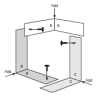
Building a 3-D Space Maze: Escher Staircase
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 95 of the PDF), learners create Escher Staircase models similar to those that were used by Neurolab's Spatial Orientation Team to investigate the processing of information about
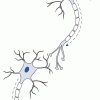
What Is a Neuron?
Source Institutions
This neuroscience activity introduces learners to how messages are sent and received by neurons. Learners use modeling clay and pipe cleaners to build model neurons.

Mirror Image
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate procedural memory.
Neurotransmitters Contain Chemicals
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners play a simple card game to learn the sequence of events in the transmission of nervous system signals.
Message in a Neuron
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners play a simple card game to learn the sequence of events in the transmission of nervous system signals.

In the News
Source Institutions
In this fun and imaginative writing assignment (page nine of the pdf), students will flex the creative side of their brains to learn more about the laws of motion and the scientific process.

Jumpin' the Gap
Source Institutions
In this simulation of synapses, learners act out communication at the neural level by behaving as pre-synaptic vesicles, neurotransmitters, post-synaptic receptors, secondary messengers and re-uptake

Raising the Level of Carbon Dioxide in Your Blood
Source Institutions
In this activity (on page 146 of the PDF), learners will explore the effects of increased carbon dioxide in the bloodstream.
Neural Network Signals
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create an electrical circuit and investigate how some dissolved substances conduct electricity.

The Geophysical Light/Dark Cycle
Source Institutions
This is an activity (located on page 131 of the PDF) related to sleep and circadian rhythms as well as space travel.

Vestibular-Ocular Reflex
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will perform various investigations to understand the vestibular-ocular reflex and learn about the importance of visual cues in maintaining balance.

How Long Can You Hold Your Breath?
Source Institutions
In this activity (on page 142 of the PDF), learners will compare breathing rates before and after hyperventilation to explore how reduced carbon dioxide levels in the blood lower the need to breathe.
