Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 22
Space Stations: Measure Up!
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners work in pairs to measure each other's ankles with lengths of string.

Experiencing Parallax With Your Thumb
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate parallax, a method used to measure distances to stars and planets in the solar system.
Launch Altitude Tracker
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners construct hand-held altitude trackers. The device is a sighting tube with a marked water level that permits measurement of the inclination of the tube.
Light on Other Planets
Source Institutions
In this math-based activity, learners model the intensity of light at various distances from a light source, and understand how astronomers measure the amount of sunlight that hits our planet and othe
Globe at Night
Source Institutions
In this international citizen science activity, learners measure their night sky brightness and submit their observations into an online database.
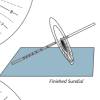
Equatorial Sundial
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make an equatorial sundial, which is simple to construct and teaches fundamental astronomical concepts. Learners use the provided template and a straw to build the sundial.

Space Stations: Sponge Spool Spine
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners simulate what happens to a human spine in space by making Sponge Spool Spines (alternating sponge pieces and spools threaded on a pipe cleaner).

Radar Mapping: What's in the Box?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners mimic remote sensing. Learners use a stick to measure the distance to a "planet surface" they cannot see, and create their own map of the landscape.

Meteoroids and the Craters They Make
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate the formation of craters. Learners will examine how the size, angle and speed of a meteorite's impact affects the properties of craters.
Finding the Size of the Sun and Moon
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build a simple pinhole viewer. They use this apparatus to project images from a variety of light sources, including a candle, the Sun, and the Moon.

Jiggly Jupiter
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build edible models of Jupiter and Earth to compare their sizes and illustrate the planets' internal layers.

The Pull of the Planets
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners model the gravitational fields of planets on a flexible surface.
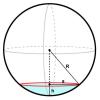
Mass, Area, Volume
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 18 of PDF), learners will measure the volume of impact craters created by projectiles of different masses.
Heavyweight Champion: Jupiter
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners confront their perceptions of gravity in the solar system.

Dunking the Planets
Source Institutions
In this demonstration, learners compare the relative sizes and masses of scale models of the planets as represented by fruits and other foods.

Ancient Sun Observations
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make their own Sun tracker to explore how ancient civilizations around the world studied the Sun.

Delta, Delta, Delta
Source Institutions
In this experiment, learners construct an equilateral triangle using graph paper, a pencil, protractor and ruler. They also make a "laser triangle" using a laser pointer and front-silvered mirrors.

Size, Mass, Area, and Volume
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 23 of PDF), learners conduct an experiment to determine how the size and mass of a projectile affects the area and the volume of an impact crater.

Lift Off!
Source Institutions
This activity (on page 2 of the PDF under SciGirls Activity: Lift Off) is a full inquiry investigation into the engineering challenges of sending scientific sensors into space.
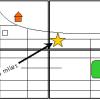
Solar System in My Neighborhood
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners shrink the scale of the vast solar system to the size of their neighborhood.
