Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 63

A Funny Taste
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore the different salinities of various sources of water by taste-testing.

Water, Water Everywhere
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners estimate how much water they think can be found in various locations on the Earth in all its states (solid, liquid, and gas) to discover the different water ratios in the Ea

Home Water Audit
Source Institutions
This activity offers learners and their families several ways to raise their awareness together about home water.

Comparing the Density of an Object to the Density of Water
Source Institutions
Learners compare the weight of equal volumes of wax, water, and clay. Learners discover that since the wax weighs less than an equal volume of water, it is less dense than water and will float.

Penny Drop
Source Institutions
In this quick activity about the properties of water (page 1 of PDF under SciGirls Activity: Malformed Frogs), learners will use an eyedropper to slowly place one drop of water at a time onto a penny,
Big and Little Cups
Source Institutions
In this indoor or outdoor water activity, learners pour water from small cups to large cups and containers. In doing so, they discover water takes the shape of its container.

Water Walk
Source Institutions
Learners take a field trip along a local body of water and conduct a visual survey to discover information about local land use and water quality.

Shower Estimation
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners calculate their water usage (in cups and galloons) during an average shower. Learners also chart and analyze water usage during showers in their households.

Measure the Speed of a Water Leak
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 2 of PDF under GPS: Glaciers Activity), learners will measure the rate at which water streams out of a leaky cup.
Earth's Water: A Drop in Your Cup
Source Institutions
This creative lesson plan provides a visual way for learners to gain knowledge about the finite amount of fresh water on Earth and encourages the discussion of the various ways to conserve this resour

Earth's Water: A Drop in Your Cup
Source Institutions
This creative lesson plan provides a visual way for learners to gain knowledge about the finite amount of fresh water on Earth and encourages the discussion of the various ways to conserve this resour

Solar Water Heater
Learners work in teams to design and build solar water heating devices that mimic those used in residences to capture energy in the form of solar radiation and convert it to thermal energy.
Making Rivers
Source Institutions
In this outdoor water activity, learners explore how to change the direction of water flow. Learners make puddles in dirt or use existing puddles and sticks to make water flow.

Toast a Mole!
Source Institutions
In this quick activity, learners drink Avogadro's number worth of molecules - 6.02x10^23 molecules!
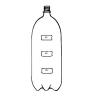
Under Pressure
Source Institutions
In this experiment, learners examine how pressure affects water flow. In small groups, learners work with water and a soda bottle, and then relate their findings to pressure in the deep ocean.
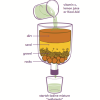
Water Clean-up
Source Institutions
This is an activity (located on page 3 of the PDF under Water Clean-up Activity) about the use of reduction agents to decontaminate ground water.

Leaf it to Me
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners observe the effect of transpiration as water is moved from the ground to the atmosphere.
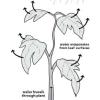
Plant Piping
Source Institutions
Learners build models to learn about the special cells and structures that plants use to move water from their roots up through the stems and leaves.

Atmospheric Collisions
Source Institutions
In this activity/demonstration, learners observe what happens when two ping pong balls are suspended in the air by a hair dryer. Use this activity to demonstrate how rain drops grow by coalescence.

Super Soaking Materials
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will test cups full of potting soil, sand, and sphagnum moss to see which earth material is able to soak up the most water.
