Search Results
Showing results 1 to 13 of 13
What Does Life Need to Live?
Source Institutions
In this astrobiology activity (on page 11 of the PDF), learners consider what organisms need in order to live (water, nutrients, and energy).

Conductivity: Salty Water
Source Institutions
Water, whether fresh or salty, serves as one of the best electrical conductors on the planet. Does salt effect its conductivity?

Be A Pasta Food Scientist
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners of all ages can become food scientists by experimenting with flour and water to make basic pasta.

Indicating Electrolysis
Source Institutions
Electrolysis is the breakdown of water into hydrogen and oxygen. This Exploratorium activity allows learners to visualize the process with an acid-based indicator.

Dip Dip, Hooray
Source Institutions
Lakes, streams and other freshwater bodies are a habitat for lots of living things, big and small.

Convection Current
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make their own heat waves in an aquarium.
What Molecules Make the Holes in Bread?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will discover why there are holes in bread.
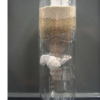
Water Treatment
Source Institutions
Water treatment on a large scale enables the supply of clean drinking water to communities.

Runaway Runoff
Source Institutions
When it rains, water can collect on top of and seep into the ground. Water can also run downhill, carrying soil and pollution with it.

Clear Water, Murky Water
Source Institutions
How do scientists measure how clear or murky water in a lake is? How does water clarity (clearness) affect what lives in the lake?

Stick to It: Adhesion II
Source Institutions
Water sticks to all kinds of things in nature — flowers, leaves, spider webs - and doesn't stick to others, such as a duck's back.
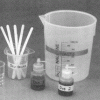
To Dye For
Source Institutions
Learners add two dyes to mineral oil and water, and then compare their miscibility (how well they mix) in each.

Geyser
Source Institutions
This Exploratorium activity can be used in many contexts because geysers are great opportunities for learning about heat and temperature changes as well as geological/space science phenomena.
