Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 44

Hot Equator, Cold Poles
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use multiple thermometers, placed at different angles, and a lamp to investigate why some places on Earth's surface are much hotter than others.

Battleships: Searching Algorithms
Source Institutions
This activity explores the main algorithms that are used as the basis for searching on computers, using different variations on the game of battleships.

Glaciers
Source Institutions
In this online activity, learners adjust mountain snowfall and temperature to see how glaciers grow and shrink. They will use scientific tools to measure thickness, velocity and glacial budget.
Making a One-Second Timer
Source Institutions
This lab activity has learners create a pendulum with a one-second period.

Cookie Mining
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore the economics of coal mining as you they use fake money to purchase mining tools, attempt to carefully mine their cookies, sell their chocolate chip ore, and try to

Counting With Quadrants
Source Institutions
Millions of organisms can live in and around a body of water.
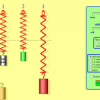
Masses & Springs
Source Institutions
In this online activity, learners use a realistic mass and spring laboratory. They hang masses from springs and adjust the spring stiffness and damping.

Home Water Audit
Source Institutions
This activity offers learners and their families several ways to raise their awareness together about home water.

Detect Solar Storms
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build their own magnetometer using an empty soda bottle, magnets, laser pointer, and household objects.
The Drake Equation
Source Institutions
In this math activity, based on the research of famed astronomer Frank Drake, learners calculate the possibilities of finding intelligent life elsewhere in the universe besides Earth.

Artificial Intelligence: The Intelligent Piece of Paper
Source Institutions
This activity explores what it means for a computer to be intelligent and introduces the topic of what a computer program is and how everything computers do simply involves following instructions writ

Bubbles: Using Controls
In this experiment, learners use JOY liquid detergent and glycerin to make the largest bubble they can that lasts 15 seconds.

Breaking the Code: Mayan Math
Source Institutions
This is a lesson plan for an activity in which learners, playing the role of archeologists, use math concepts about number bases to decipher the Dresden Codex, an ancient Mayan document.

Paper Chain Testing
Source Institutions
Learners will do an experiment to determine which type of paper is strongest while focusing on variables and collecting data.

Stabilization Wedges Game
Source Institutions
This game introduces learners to the scale of the greenhouse gas problem, plus technologies that already exist to dramatically reduce our carbon emissions and prevent climate change.

Monitoring Amphibians
Source Institutions
In this field study, learners discover how to collect data in the field and how their efforts can help certain animals, specifically, amphibians.

Clear Water, Murky Water
Source Institutions
How do scientists measure how clear or murky water in a lake is? How does water clarity (clearness) affect what lives in the lake?

pH Scale
Source Institutions
In this online interactive simulation, learners will test the pH of liquids like coffee, spit, and soap to determine whether each is acidic, basic, or neutral.

Edible Glass
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover the principles of edible glass by making a supersaturated sugar solution.

Seas in Motion
Source Institutions
In this outdoor, beach activity, learners use tennis balls, water balloons and other simple devices to investigate the movement of waves and currents off a sandy beach.
