Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 33

Lava Layering: Making and Mapping a Volcano
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover how geologists use stratigraphy, the study of layered rock, to understand the sequence of geological events.

From the Internet to Outer Space
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will use Google Sky to observe features of the night sky and share their observations.

Space Stations: Follow the Bouncing Ball!
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners predict whether a ball on Earth or a ball on the Moon bounces higher when dropped and why.

Future Moon: The Footsteps of Explorers
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners drop impactors onto layers of graham crackers!

Infant Moon: Moon Mix!
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate the Moon's infancy and model how an ocean of molten rock (magma) helped shape the Moon that we see today.
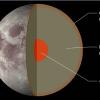
Recipe for a Moon
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover that the Moon, like Earth, is made up of layers of different materials. Learners work in teams to make models of the interiors of the Moon and Earth.

Space Stations: Beans in Space
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners perform 20 arm curls with cans that simulate the weight of beans on Earth versus the weights of the same number of beans on the Moon and in space.

The Thousand-Yard Model
Source Institutions
This is a classic exercise for visualizing the scale of the Solar System.
Shapes and Angles
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 7 of PDF), learners will identify the general two-dimensional geometric shape of the uppermost cross section of an impact crater.

Make An Impact
Source Institutions
In this hands-on activity, learners simulate the crashing and smashing of a meteor impact using household cooking supplies.
Finding the Size of the Sun and Moon
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build a simple pinhole viewer. They use this apparatus to project images from a variety of light sources, including a candle, the Sun, and the Moon.

Why Does the Moon Have Phases?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use a simple 3D model to discover why the Moon has phases.

Kid Moon: Splat!
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners model ancient lunar impacts using water balloons.

Teen Moon: Moon Ooze
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners model how the Moon's volcanic period reshaped its earlier features.

Moon's Long History: Impact Paintings
Source Institutions
In this activity, pairs of learners model how scientists use craters to determine the ages of lunar surfaces. One partner keeps time while the other creates a painting for the other to interpret.

Eclipse: How can the little Moon hide the giant Sun?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how distance can affect the way we perceive the size of an object.

Size, Mass, Area, and Volume
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 23 of PDF), learners conduct an experiment to determine how the size and mass of a projectile affects the area and the volume of an impact crater.

Size it Up
Source Institutions
Learners investigate why the Sun and Moon appear the same size in the sky even though the Sun is over 400 times larger in diameter.
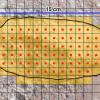
Angles and Area
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 10 of PDF), learners approximate the area of the uppermost cross section of an impact crater using a variety of square grids.

Balloon Impacts
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners measure the diameter of their water balloons, model an impact, measure the diameter of the “crater” area, and determine the ratio of impactor to crater.
