Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 60

Lava Layering: Making and Mapping a Volcano
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover how geologists use stratigraphy, the study of layered rock, to understand the sequence of geological events.

Modeling Day and Night
Source Institutions
In this activity (on page 1 of the PDF), learners make a "mini-globe" to investigate the causes of day and night on our planet.

Counting With Quadrants
Source Institutions
Millions of organisms can live in and around a body of water.
The Earth's Timeline
Source Institutions
In this group activity, learners will mark important developments of life on Earth on a timeline (each foot in length representing 200 million years).

Jiggly Jupiter
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build edible models of Jupiter and Earth to compare their sizes and illustrate the planets' internal layers.

Space Stations: Follow the Bouncing Ball!
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners predict whether a ball on Earth or a ball on the Moon bounces higher when dropped and why.
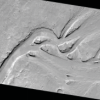
Mars from Above: Carving Channels
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create channel features with flowing water, comparing their observations to real images of Mars and Earth taken by satellites/orbiters.
Big Time Tour
Source Institutions
In this activity (on pages 16-21), learners get a sense of geological time by understanding how big a million is.

Weather Stations: Temperature and Pressure
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover the relationship between temperature and pressure in the lower atmospheres of Jupiter and Earth.

Make Your Own Sundial
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate the Earth's rotation and how to tell the time of day without a clock. Thsi simple activity only requires a paper plate, a pencil, and sunshine.

Human-powered Orrery
Source Institutions
In this space science activity, learners work together to create a human-powered orrery to model the movements of the four inner planets.

Space Rocks!: A Meteorite Game
Source Institutions
In this board game, learners explore the origins of meteors, meteoroids, and meteorites as well as the their characteristics and importance. They also discover some misconceptions about meteors.
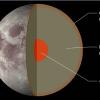
Recipe for a Moon
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover that the Moon, like Earth, is made up of layers of different materials. Learners work in teams to make models of the interiors of the Moon and Earth.

Space Stations: Beans in Space
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners perform 20 arm curls with cans that simulate the weight of beans on Earth versus the weights of the same number of beans on the Moon and in space.

The Thousand-Yard Model
Source Institutions
This is a classic exercise for visualizing the scale of the Solar System.

Earthquake Energy
Source Institutions
In this geology activity (page 3 of the PDF), learners simulate an earthquake with little more than an elastic band and drinking straws.

A Crayon Rock Cycle- Metamorphic
Source Institutions
This is part 2 of the three-part "Crayon Rock Cycle" activity and must be done after part 1: Sedimentary Rocks. In this activity, learners explore how metamorphic rocks form.

Mars from Above: Viewing Volcanoes
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create volcanoes like those they have examined on Earth and Mars through images taken by spacecraft.

A Crayon Rock Cycle - Igneous
Source Institutions
This is part 3 of the three-part "Crayon Rock Cycle" activity. Before starting this section, learners must have completed part 1: sedimentary rock and part 2: metamorphic rocks.

Detect Solar Storms
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build their own magnetometer using an empty soda bottle, magnets, laser pointer, and household objects.
