Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 25
Why Are Two Eyes Better Than One?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how their depth perception would be affected if they only had one eye. Learners work in pairs and attempt to drop a penny in a cup with one eye covered.

Stroboscope
Source Institutions
In this activity (posted on March 20, 2011), learners follow the steps to construct a stroboscope, a device that exploits the persistence of vision to make moving objects appear slow or stationary.

Seeing Is Believing
Source Institutions
This activity is designed to accompany the PBS documentary about African-American chemist "Percy Julian: Forgotten Genius." Learners look through two cups with small holes in them to simulate what it'

Reaction Time
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct an experiment to test how fast they can react. Learners try to catch a piece of paper with a ruler printed on it (or a ruler) as quickly as they can.

X-Ray Vision?
Source Institutions
In this activity (13th on the page), learners complete a simple illusion trick to see through their own hand.
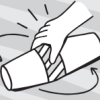
Magic Disc
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create an optical illusion by spinning two attached cups. A round ball seems to magically appear when the cups spin.

Phenakistascope
Source Institutions
In this optics activity, learners build an animation tool to make mini movies. When you spin a phenakistascope, the pictures move so quickly that your eyes and brain can't separate the images.
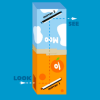
Periscope
Source Institutions
In this optics activity, learners build a spy tool to secretly view things over walls or around corners.

Measure Your Ability to See
Source Institutions
In this exercise (Activity #2 on page), learners test their distance vision to evaluate their overall eyesight.
Train Your Brain
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners play a trick on their own brain to see if the brain can learn to ignore distracting input. Colors and words are used to play the visual trick, known as a Stroop Test.

Penny Cup Game
Source Institutions
In this optics activity, learners conduct an experiment to find out why two eyes are better than one!

Afterimage
Source Institutions
In this optics activity, learners investigate afterimages.

Peripheral Vision
Source Institutions
In this optics activity, learners conduct an experiment to explore peripheral vision. Learners collect data about their ability to see shapes, colors, or letters using their peripheral vision.

Think Fast!
Source Institutions
This is a quick and simple demonstration about reflexes (fourth activity on the page). One learner stands behind a see-through barrier like a window or wire screen.
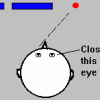
The Blind Spot
Source Institutions
In this activity (1st on the page), learners find their blind spot--the area on the retina without receptors that respond to light.

Dark Adaptation
Source Institutions
In this activity (6th on the page), learners investigate how photoreceptors in the eye (rods and cones) "adapt" to low light conditions.
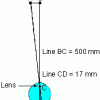
Measuring Your Blind Spot
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners calculate the width (horizontal diameter) of the blind spot on their retina. Learners make a blind spot tester using a piece of notebook paper.

Depth Perception
Source Institutions
In this easy demonstration (3rd on the page), learners explore depth perception by conducting a test with two pencils.

Arrows
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners surprise their eyes with an optical illusion involving arrows made out of pipe cleaners.
Drop IT!: Depth Perception
Source Institutions
These two activities (4th on the page) demonstrate the importance of two eyes in judging depth.
