Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 29

The Boxes Go Mobile
Source Institutions
Learners display their findings after a study of surface area and volume. They build a mobile to show a commercially available box and a constructed cubical box of the same volume.
Geometry and Spatial Relations: Mirror, Mirror
Source Institutions
In this math lesson, learners use hinged mirrors to discover that regular polygons are composed of triangles tessellating around a center point.
Walking Polygons
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners walk the sides and interior angles of various polygons drawn on the playground. As they do so, learners practice rotating clockwise 180° and 360°.
Loopy Geometry
Source Institutions
Discover geometry by creating shapes from loops of paper. In this activity, paper loops transform to give you totally new structures when you cut them.
Shapes and Angles
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 7 of PDF), learners will identify the general two-dimensional geometric shape of the uppermost cross section of an impact crater.
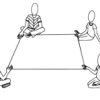
String Shapes
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners work together to make polygons (many-sided shapes) with string. Learners sit on the floor and hold onto a piece of string slid between their thumbs and index fingers.
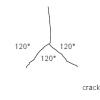
Playground Patterns of Cracks
Source Institutions
In this math activity, learners observe and sketch cracking patterns in pavement.
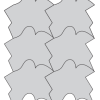
Making a Translation Tessellation
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners slide shapes to create unusual tiled patterns.

Make A Map for A Treasure Hunt
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will explore how maps can provide information about a place and help us find our way from one location to another.

New Boxes from Old
Source Institutions
Learners determine the surface area and volume of two identical boxes, and then figure out the dimensions of a cubical box with the same volume.

The Shadow Knows II
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will measure the length of a shadow and use the distance from the equator to calculate the circumference of the earth.
Building Houses: Build a Cardboard Tube House
Source Institutions
Build a house you can fit inside, using cardboard tubes.
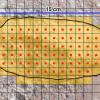
Angles and Area
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 10 of PDF), learners approximate the area of the uppermost cross section of an impact crater using a variety of square grids.
Special Effects: Titanic and Beyond
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate how geometry plays a role in perspective.
Exploring Tessellations (Grades 6-8)
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners design unique tiles and make repeating patterns to create tessellations. This activity combines the creativity of an art project with the challenge of solving a puzzle.
The Right Fit
Source Institutions
In this math activity, learners trace their hands and estimate the number of beans that can fit into their hand tracings. Then, learners glue the beans to the tracing to test out their estimations.
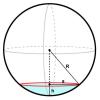
Mass, Area, Volume
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 18 of PDF), learners will measure the volume of impact craters created by projectiles of different masses.
Peppy's Day in the Park
Source Institutions
In this math activity, learners build Peppy the dog the best trail and park for running around.
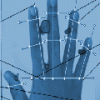
Hand Biometrics Technology
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how engineers incorporate biometric technologies into products as well as the challenges of engineers who must weigh privacy, security and other issues when designin

Tri, Tri Again
Source Institutions
Learners estimate how many small triangles will fill a larger shape. Then they use a triangle stamp (or stencil made from a file folder) to fill the larger shape with triangles.
