Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 21

Don't Crack Humpty
Source Institutions
Groups of learners are provided with a generic car base and an egg. Their mission: design a device/enclosure to protect the egg on or in the car as it rolls down a ramp with increasing slopes.

Plot the Dot: A Graphical Approach to Density
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners work in groups to determine the mass and volume of four samples: glass marbles, steel washers or nuts, pieces of pine wood, and pieces of PVC pipe.

Landing the Rover
Source Institutions
In this team design challenge (page 19-24 of PDF), learners "land" a model Lunar Rover in a model Landing Pod (both previously built in activities #3 and #4 in PDF).

Linear Functions: Mystery Liquids
Source Institutions
In this math lesson, learners analyze the density of liquids in order to explore linear functions.

Skateboard Disaster
Learners examine collisions between two skateboards carrying different masses. They learn about conservation of momentum in collisions.

Burn a Peanut
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners burn a peanut, which produces a flame that can be used to boil away water and count the calories contained in the peanut.

Hanging Around
Learners investigate weight by building a spring scale. They observe and record how it responds to objects with different masses.

Super Soaker
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 1 of the PDF under SciGirls Activity: Bogs), learners will test cups full of potting soil, sand, and sphagnum moss to see which earth material is able to soak up the most water.
Lightest and Heaviest: Sorting Algorithms
Source Institutions
Computers are often used to put lists into some sort of order—for example, names into alphabetical order, appointments or e-mail by date, or items in numerical order.

Size, Mass, Area, and Volume
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 23 of PDF), learners conduct an experiment to determine how the size and mass of a projectile affects the area and the volume of an impact crater.

Super Soaking Materials
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will test cups full of potting soil, sand, and sphagnum moss to see which earth material is able to soak up the most water.

Rubber Band newton Scale
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make a simple spring-like scale using a rubber band instead of a spring, and calibrate the scale in newtons (N).

Weight in Space
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners are challenged to calculate their own weight on various planets using a scale and calculator. Older learners may be challenged to do so without using calculators.

Balanced Budget Chemistry
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners balance chemical equations and discover the law of conservation of mass. Learners use coins to model molecules to balance the equations.
Design a Lunar Rover!
Source Institutions
In this team design challenge (page 2-10 of PDF), learners design and build a model of a Lunar Transport Rover that will carry equipment and people on the surface of the Moon.
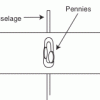
Lift Experiment
Source Institutions
In this experiment, learners investigate how the size of a wing affects lift. Learners count the number of pennies an egg crate plane wing can hold until the plane will no longer fly.

Having a Gas with Cola
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners measure the amount of carbon dioxide in a carbonated drink.

Ship the Chip
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore engineering package designs that meet the needs of safely shipping a product.
Design a Landing Pod!
Source Institutions
In this team design challenge (page 11-18 of PDF), learners design and build a Landing Pod for a model Lunar Rover (previously built in activity on page 1-10 of PDF).

