Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 31
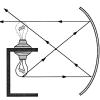
Touch the Spring (Lightbulb)
Source Institutions
In this activity, a lightbulb is placed in front of a concave mirror. The actual lightbulb is not visible to the viewer, but the viewer can see the mirror image of the lightbulb formed in space.

Mirrors and Images
Source Institutions
In this optics activity, learners explore how many objects they can see in a set of mirrors (hinged like a book) at various angles.

Earth's Energy Cycle: Albedo
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners experiment and observe how the color of materials that cover the Earth affects the amounts of sunlight our planet absorbs.

Cylindrical Mirror
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create a cylindrical mirror to see themselves as others see them.

Morphing Butterfly
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how nanosized structures can create brilliant color.
What is Nanotechnology?
Source Institutions
In this activity related to nanotechnology, learners observe some of the effects that result from creating a thin layer of material several nanometers thick.
Liquid Crystals Interact with Light!
Source Institutions
In this two-part activity, learners explore the properties of liquid crystals, which are responsible for why mood rings change color.
Soda Can Mirrors
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how pictures change in curved mirrors. Learners make cylindrical mirrors by wrapping Mylar around soda cans.
Multiple Reflections
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how mirrors reflect light and change the way we see things.

CD Spectrometer
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use a compact disc to make a spectrometer, an instrument used to measure properties of light.

Polarized Sunglasses
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how polarizing sunglasses can help diminish road glare.

Exploring Tessellations (Grades K-2)
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners repeat patterns in two and three dimensions to create tessellations. This activity combines the creativity of an art project with the challenge of solving a puzzle.

Cardboard Opaque Projector
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners construct a projector out of cardboard to view their favorite images (such as storybook illustrations) on the wall.

Corner Reflector
Source Institutions
In this optics/mathematics activity, learners use two hinged mirrors to create a kaleidoscope that shows multiple images of an object.

Total Internal Reflection
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use a laser pointer, empty soda bottle, rubber plug and water to demonstrate total internal reflection.

Animal Reflection Response
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 1 of the PDF under SciGirls Activity: Horse Ears), learners observe how an animal responds to its own reflection.

Cardboard Box Camera Obscura
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners construct a device that projects images onto a surface, so they can trace landscapes and other sights.

Super Sleuths
Source Institutions
In this physical sciences activity, learners use science to solve a "crime." Learners collect trace evidence (glitter) and explore its characteristics, such as color, size, shape, and light reflection
Exploring Tessellations (Grades 3-5)
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners repeat patterns in two and three dimensions to create tessellations.
Exploring Tessellations (Grades 6-8)
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners design unique tiles and make repeating patterns to create tessellations. This activity combines the creativity of an art project with the challenge of solving a puzzle.
