Search Results
Showing results 1 to 18 of 18

Zero-Energy Housing
In this activity, learners investigate passive solar building design with a focus solely on heating.

Supernovae in the Lives of Stars
Source Institutions
Many people think the different stages in the life of a star are actually different types of stars, rather than just stages in the life of a single star.

Portable Sundial
Source Institutions
Learners construct one or more of the following kinds of sundials: a shadow plot, a horizontal sundial, and a diptych sundial.

Solar Energy
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 11 of PDF), learners compare the air pressure within a dark and a light bottle both heated by the sun, and discover that solar energy can be collected and stored in many ways

Solar Water Heater
Learners work in teams to design and build solar water heating devices that mimic those used in residences to capture energy in the form of solar radiation and convert it to thermal energy.

Crystal Creations: Grow Spikes of Crystals in the Sun
Source Institutions
This activity shows you how to make amazing crystal spikes using Epsom salt and the sun.
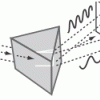
Rainbow in the Room
Source Institutions
This activity generates learner excitement about light through the creation of a room-sized rainbow.
Any Year Calendars
Source Institutions
This PDF contains 12 calendars (12 months). Each month contains activities about math. Things to do on familiar holidays (like July 4), less common holidays (like Backward Day), and any day.

The Shadow Knows II
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will measure the length of a shadow and use the distance from the equator to calculate the circumference of the earth.

Toasty Wind
Source Institutions
In this quick activity, learners use a toaster to investigate the source for the Earth's wind. Learners hold a pinwheel above a toaster to discover that rising heat causes wind.

What Causes Wind?
Source Institutions
In this sunny day experiment, learners measure and compare how quickly light and dark colored materials absorb heat.

Sun Cookies
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use candy pieces and a cookie to make an accurate model of the Sun they can eat. Parts of the delicious model include solar granules, sunspots, and solar prominences.

Solar Spin
Source Institutions
A group of learners models the Sun shining on the Earth. By rotating the Earth, they demonstrate how the Sun only shines on a portion of the Earth at a time.
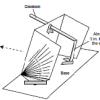
Using a Sundial
Source Institutions
In this activity (on page 12 of the PDF), learners make a sundial (shadow clock) appropriate for their geographic location in the northern hemisphere and use it to tell time.

Exploring Earth: Bear’s Shadow
Source Institutions
“Exploring Earth: Bear’s Shadow” is a hands-on activity designed primarily for young visitors and their families. Participants move a flashlight around an object to make and experiment with shadows.
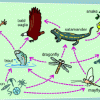
What's for Dinner?
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 5 of the PDF), learners will create a food web and explore food sources for different organisms. They will identify relationships between organisms in an ecosystem.

Snake
Source Institutions
In this physics activity (page 4 of the PDF), learners will construct their own spiral "snake" and use it to explore the relationship between heat and kinetic energy.
Finding the Right Crater
Source Institutions
This quick demonstration (on page 11 of PDF) allows learners to understand why scientists think water ice could remain frozen in always-dark craters at the poles of the Moon.
