Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 36

Changing the Density of a Liquid: Adding Salt
Source Institutions
Learners see that a carrot slice sinks in fresh water and floats in saltwater.

Comparing the Density of an Object to the Density of Water
Source Institutions
Learners compare the weight of equal volumes of wax, water, and clay. Learners discover that since the wax weighs less than an equal volume of water, it is less dense than water and will float.
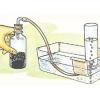
Pneumatic Trough
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build a "pneumatic trough," a laboratory apparatus used for collecting pure gas samples over water.

Defining Density
Source Institutions
In this introductory demonstration and activity, learners are introduced to the concept of density as they explore a rock and a wooden block in water.

Changing the Density of an Object: Changing Shape
Source Institutions
Learners will see that changing the shape of an object, like a clay ball, that is more dense than water, can affect whether the object will sink or float.

Plot the Dot: A Graphical Approach to Density
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners work in groups to determine the mass and volume of four samples: glass marbles, steel washers or nuts, pieces of pine wood, and pieces of PVC pipe.

Inverse Functions: Pennies, Pressure, Temperature, and Light
Source Institutions
The major goal of this math lesson is to have learners collect data from a variety of experiments, determine what models best fits their data, and explain why their models are best.

The Liquid Rainbow
Source Institutions
Learners are challenged to discover the relative densities of colored liquids to create a rainbow pattern in a test tube.

Linear Functions: Mystery Liquids
Source Institutions
In this math lesson, learners analyze the density of liquids in order to explore linear functions.

Ready, Set, Fizz!
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore the chemical reaction between water and effervescent antacid tablets. This hands-on activity models how a material can act differently when it's nanometer-sized.

Inflate-a-mole
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct an experiment to find the volume of one mole of gas. Learners capture sublimated gas from dry ice in a ziploc bag and use water displacement to measure its volume.

Make a Salt Volcano (Lava Lite)
Source Institutions
This activity about density provides instructions for making a miniature "lava lite" with just salt, oil, water, and food coloring.

Size, Scale and Models
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners take measurements and create charts to learn about the size of dinosaurs and their relative scale to humans.

What's So Special about Water: Solubility and Density
Source Institutions
In this activity about water solubility and density, learners use critical thinking skills to determine why water can dissolve some things and not others.

Rates of Change: Bottles and Divers
Source Institutions
In this math lesson (page 2 of the PDF), learners use bottles of various shapes to explore the abstract concept of rate of change.

Test the Finger Wrinkle Hypothesis
Source Institutions
Learners create a tool to measure how well they grip a wet object when their fingers are smooth versus wrinkly. Are smooth or wrinkly fingers better at holding on to the object?

Size, Mass, Area, and Volume
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 23 of PDF), learners conduct an experiment to determine how the size and mass of a projectile affects the area and the volume of an impact crater.

Changing the Density of a Liquid: Heating and Cooling
Source Institutions
Learners investigate how the temperature of water affects its density.

Changing the Density of an Object: Adding Material
Source Institutions
Learners see that a can of regular cola sinks while a can of diet cola floats. As a demonstration, bubble wrap is taped to the can of regular cola to make it float.

Sink It
Source Institutions
Learners classify a variety of objects by their characteristics. They then design an experiment to determine which objects float or sink in water and add this characteristic to their classification.
