Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 42
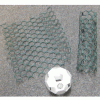
Tiny Tubes
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make "totally tubular" forms of carbon. Learners use chicken wire to build macro models of carbon nanotubes.

Find the Fat
Source Institutions
Fat is a very important component in our diet. It's the most efficient source of energy in our bodies, and plays an important role in the flavor of foods.

CD Spinner
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create a simple “top” from a CD, marble and bottle cap, and use it as a spinning platform for a variety of illusion-generating patterns.

Your Age on Other Worlds
Source Institutions
Did you know that you would be a different age if you lived on Mars? It's true!

Take It From The Top: How Does This Stack Up?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore center of gravity, or balance point, of stacked blocks.

Cylindrical Mirror
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create a cylindrical mirror to see themselves as others see them.

Make a Sun Clock: Tell Time with the Sun
Source Institutions
Before there were clocks, people used shadows to tell time. In this outdoor activity, learners will discover how to tell time using only a compass, a pencil, a handy printout, and a sunny day.

Life Size: Line 'em up!
Source Institutions
In this activity on page 1 of the PDF, learners compare the relative sizes of biological objects (like DNA and bacteria) that can't be seen by the naked eye.

Fast Rusting
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct an experiment to find out if steel wool will weigh more or less when it is burned. Learners will explore the effects of oxidation and rusting on the steel wool.

Height Sight
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build a tool called an inclinometer that can find the height of any distant object, from a tree to the North Star.

Throwing Pi
Source Institutions
In this calculus activity, learners use a classic problem of geometrical probability to find an important mathematical constant (pi).

Burn a Peanut
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners burn a peanut, which produces a flame that can be used to boil away water and count the calories contained in the peanut.
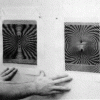
Moiré Patterns
Source Institutions
In this activity about light and perception, learners create and observe moire patterns.
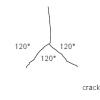
Playground Patterns of Cracks
Source Institutions
In this math activity, learners observe and sketch cracking patterns in pavement.

Polarized Sunglasses
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how polarizing sunglasses can help diminish road glare.
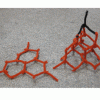
Carbon Configurations
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use geometry to predict the shape of carbon. Learners twist and attach chenille stem pieces that represent bonds between different carbon atoms.

Corner Reflector
Source Institutions
In this optics/mathematics activity, learners use two hinged mirrors to create a kaleidoscope that shows multiple images of an object.

"Baseketball": A Physicist Party Trick
Source Institutions
This trick from Exploratorium physicist Paul Doherty lets you add together the bounces of two balls and send one ball flying.

Oil Spot Photometer
Source Institutions
In this math activity related to light, learners assemble a photometer and use it to estimate the power output of the Sun.
Traveling Networks
Source Institutions
In this geometry activity, learners explore networks painted on playgrounds, such as a four square court, and draw their own.
