Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 29

Why Do Eclipses Happen?
Source Institutions
This fun and simple hands-on astronomy activity lets learners create 3D models of the Earth, Moon and Sun to demonstrate solar and lunar eclipses.

The Pull of the Planets
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners model the gravitational fields of planets on a flexible surface.

Space Stations: Sponge Spool Spine
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners simulate what happens to a human spine in space by making Sponge Spool Spines (alternating sponge pieces and spools threaded on a pipe cleaner).

Make a Sun Clock: Tell Time with the Sun
Source Institutions
Before there were clocks, people used shadows to tell time. In this outdoor activity, learners will discover how to tell time using only a compass, a pencil, a handy printout, and a sunny day.

Solar Cell Simulation
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners model the flow of energy from the sun as it enters a photovoltaic cell, moves along a wire and powers a load.

Searching for Life
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discuss how life is defined and conduct a simple experiment, looking for signs of life in three different “soil” samples.

Zero-Energy Housing
In this activity, learners investigate passive solar building design with a focus solely on heating.

Radar Mapping: What's in the Box?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners mimic remote sensing. Learners use a stick to measure the distance to a "planet surface" they cannot see, and create their own map of the landscape.

Human-powered Orrery
Source Institutions
In this space science activity, learners work together to create a human-powered orrery to model the movements of the four inner planets.

Future Moon: The Footsteps of Explorers
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners drop impactors onto layers of graham crackers!

Space Stations: Beans in Space
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners perform 20 arm curls with cans that simulate the weight of beans on Earth versus the weights of the same number of beans on the Moon and in space.
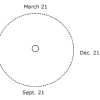
Modeling the Seasons
Source Institutions
This activity provides instructions for learners to create models of the Earth and then to model a "day" on Earth as well as modeling the seasons.

Rover Races
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners experience some of the challenges of "tele-operating" a robotic vehicle on another planet when they design and execute a series of commands to guide a human "rover" through

Does the Moon Rotate?
Source Institutions
This fun and simple hands-on astronomy activity lets learners make 3-dimensional models of the Earth and Moon.

Model the Sun and Earth
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make scale models of the Sun and Earth out of paper mache.

Light is Made of Colors
Source Institutions
Learners observe different light sources, outdoors and indoors, using prism glasses (diffraction glasses) and color filters.

Why Does the Moon Have Phases?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use a simple 3D model to discover why the Moon has phases.
Crater Maker
In this activity (on pages 6-11), learners work as a team to investigate how impact craters on Earth, the Moon or other planets take shape and what patterns they make.
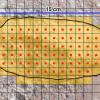
Angles and Area
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 10 of PDF), learners approximate the area of the uppermost cross section of an impact crater using a variety of square grids.

Space Jell-O
Source Institutions
Albert Einstein proved that space bends around anything that has mass. This activity uses Jell-O's ability to bend around objects as a model for space bending around planets and stars.
