Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 47

How Do Viruses Recognize a Target Cell?
Source Institutions
This activity demonstrates the specificity of viral vectors for target cells in gene therapy delivery methods using two approaches: 1) STYROFOAM® models demonstrate viral ligand binding to receptor pr

Let's Clone a Mouse, Mouse, Mouse...
Source Institutions
Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer (SCNT) is a cloning method that involves transferring a nucleus from a somatic cell of the individual to be cloned to an enucleated egg.

lambda DNA Fingerprinting Simulation
Source Institutions
The purpose of this lab activity is to demonstrate (through simulation) how DNA fingerprinting (or DNA profiling) might be used to solve a crime.

How Plants Grow
Source Institutions
In this biology activity (page 3 of the PDF), learners will explore how plants turn sunlight into food through a process called photosynthesis.

Rearing Monarchs
Source Institutions
As a long-term project, you can rear monarch butterflies at home or in a classroom.

Testing for Life's Molecules
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct tests for proteins, glucose, and starch.

Searching for Life
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discuss how life is defined and conduct a simple experiment, looking for signs of life in three different “soil” samples.
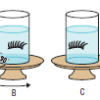
Visualizing How the Vestibular System Works
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 59 of the PDF), learners spin and observe false eyelashes in jars of water (prepared at least 1 day ahead of time) to investigate the effects of different types of motion on the
Close, Closer, Closest
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners perform an experiment that models a chromatography-like process called electrophoresis, a process used to analyze DNA.
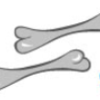
Air-filled (Pneumatic) Bone Experiments
Source Institutions
Just like birds, some dinosaurs had air-filled (pneumatic) bones, which made the dinosaurs' skeletons lighter.
Neural Network Signals
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create an electrical circuit and investigate how some dissolved substances conduct electricity.

On the Microbe Trail: An Introduction to Bacteria and Aseptic Technique
Source Institutions
In this series of exercises, learners predict the conditions necessary for bacterial growth, test their predictions and at the same time practice the aseptic techniques and safety procedures needed wh
What Does Life Need to Live?
Source Institutions
In this astrobiology activity (on page 11 of the PDF), learners consider what organisms need in order to live (water, nutrients, and energy).

The Carbon Cycle: How It Works
Source Institutions
In this game, learners walk through an imaginary Carbon Cycle and explore the ways in which carbon is stored in reservoirs and the processes that transport the carbon atom from one location to another
Modeling an HIV Particle
Source Institutions
This activity helps learners visualize the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) by constructing three-dimensional HIV particle models from paper.
Magnifying and Observing Cells
Source Institutions
In this activity related to microbes, learners make slides of cells from an onion skin and Elodea (American or Canadian waterweed) to observe under a microscope.

What's Your Blood Type?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners perform a simulated blood test procedure.
Observing Different Microbes
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use a microscope to examine three different microbes: bacteria, yeast and paramecia. Educator will need to prepare the yeast solution one day before the activity.

Pom Pom Potential
Source Institutions
In this kinesthetic activity, learners move pom-pom "ions" across a membrane to simulate how an action potential is propagated along an axon.
Forensic Science: Hair Sample Investigation
Source Institutions
This activity (on page 2 of the PDF under SciGirls Activity: Forensics) is a full inquiry investigation into how hairs from a crime scene are matched to suspects.
