Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 49
Mercury in the Environment
Source Institutions
In this environmental science lesson, learners will examine the dangers of mercury and how humans contribute to growing mercury emissions on Earth.

Wheat Evolution: Sedimentation Testing
Source Institutions
In this activity (Page 30 of PDF), learners investigate the evolution of wheat by conducting sedimentation tests on different flours.

An Apple as Planet Earth
Source Institutions
In this environmental education demonstration (page 6 of the PDF), learners will see a tangible representation of the scarcity of soil resources on earth.
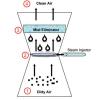
Washing Air
Learners observe and discuss a simple model of a wet scrubber, a device for cleaning industrial air pollution.

Amphibian Skin
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore the concept of permeability to better understand why amphibians are extremely sensitive to pollution.

Fuel for Living Things
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners observe what happens when yeast cells are provided with a source of food (sugar). Red cabbage "juice" will serve as an indicator for the presence of carbon dioxide.

Wheat Evolution: Dough Washing
Source Institutions
In this activity (Page 22 of PDF), learners investigate the evolution of wheat by washing different types of dough with water and comparing the results.

Wheat Evolution: Dough Rising and Baking
Source Institutions
In this activity (Page 25 of PDF), learners investigate the evolution of wheat by creating dough from different flours, observing the samples of dough as they rise, and then baking the dough.

Moving Without Wheels
In a class demonstration, learners observe a simple water cycle model to better understand its role in pollutant transport.

Hot Stuff!: Carbon Dioxide Extinguishes a Flame
In this demonstration, learners observe vinegar and baking soda creating carbon dioxide (CO2) in a bottle. The gas is poured out of a bottle onto a candle flame, putting out the candle.

Gene Switches
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how genetic switches function and the role of genetic switches in the process of evolution.

Landfill in a Bottle
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover how landfills affect the natural environment.
Make Your Own Deep-Sea Vent
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make a model of the hot water of a deep sea vent in the cold water of the ocean to learn about one of the ocean's most amazing and bizarre underwater habitats.

Hot Stuff!: Creating and Testing for Carbon Dioxide
In this demonstration, learners observe vinegar and baking soda reacting to form carbon dioxide (CO2) gas.

Hot Stuff!: Testing Ice
In this demonstration, learners compare and contrast regular water ice to dry ice (frozen carbon dioxide). Both samples are placed in a solution of acid-base indicator.
Create a Mangrove Tree
Source Institutions
In this group activity, learners will explore the characteristics, functions and uniqueness of the mangrove tree.

What-a-cycle
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners act as water molecules and travel through parts of the water cycle to discover that it is more complex than just water moving from the ground to the atmosphere.

Low-Tech Water Filter for High-Impact Clean
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners consider the water features they might enjoy at a community park--a pond, brook, water playground (or "sprayground"), or pool--and what happens to the water over time.

Battling for Oxygen
Working in groups, learners model the continuous destruction and creation of ozone (O3) molecules, which occur in the ozone layer.

Let's Bag It
Learners observe and discuss a vacuum cleaner as a model of a baghouse, a device used in cleaning industrial air pollution.
