Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 28
Where is the Sun?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners verify that the Sun appears in a different location at a specific time every day of the year with one exception: on the Equinoxes.

Modeling Day and Night
Source Institutions
In this activity (on page 1 of the PDF), learners make a "mini-globe" to investigate the causes of day and night on our planet.

The Geophysical Light/Dark Cycle
Source Institutions
This is an activity (located on page 131 of the PDF) related to sleep and circadian rhythms as well as space travel.

Morning Star and Evening Star
Source Institutions
This demonstration activity models how Venus appears from Earth.

Moonlight Serenade
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners act as the Earth and observe how different angles between the Sun, Earth, and Moon affect the phases of the moon we see each month.
My Angle on Cooling: Effects of Distance and Inclination
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover that one way to cool an object in the presence of a heat source is to increase the distance from it or change the angle at which it is faced.
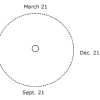
Modeling the Seasons
Source Institutions
This activity provides instructions for learners to create models of the Earth and then to model a "day" on Earth as well as modeling the seasons.

Does the Moon Rotate?
Source Institutions
This fun and simple hands-on astronomy activity lets learners make 3-dimensional models of the Earth and Moon.

Portable Sundial
Source Institutions
Learners construct one or more of the following kinds of sundials: a shadow plot, a horizontal sundial, and a diptych sundial.
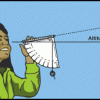
Using a Simple Astrolabe
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use an astrolabe to measure the altitude of objects. Learners will first practice taking measurements by measuring the altitude of trees and buildings.

The Shadow Knows I
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will measure the length of their shadow from the Sun and compare it three to four months later.
Any Year Calendars
Source Institutions
This PDF contains 12 calendars (12 months). Each month contains activities about math. Things to do on familiar holidays (like July 4), less common holidays (like Backward Day), and any day.

Why Does the Moon Have Phases?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use a simple 3D model to discover why the Moon has phases.

Breaking the Code: Mayan Math
Source Institutions
This is a lesson plan for an activity in which learners, playing the role of archeologists, use math concepts about number bases to decipher the Dresden Codex, an ancient Mayan document.

Moon and Stars
Source Institutions
In this craft activity, learners create a string of cut-out moons and stars.

Living Clocks
Source Institutions
In this activity about daily rhythms (on page 17 of the PDF), learners will explore circadian patterns in humans, animals and plants.

Ancient Sun Observations
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make their own Sun tracker to explore how ancient civilizations around the world studied the Sun.

Seasons and Shadows: Investigate How Shadows Shift Throughout the Year
Source Institutions
In this activity you'll see how the sun's tilt on its axis changes the length of shadows. For example, why is your shadow longer in winter than in summer?

Ancient Observatories: Timeless Knowledge Activities
Source Institutions
This lesson plan provides learners with two activities to explore the connections between events in their lives and the seasons of the year.

Make Your Own Pendulum
Source Institutions
In this demonstration about force and motion, learners will explore the forces that affect a pendulum A simple model pendulum comprised of a ball and string demonstrates how pendulums work as well as
