Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 69

Lava Layering: Making and Mapping a Volcano
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover how geologists use stratigraphy, the study of layered rock, to understand the sequence of geological events.

The Geophysical Light/Dark Cycle
Source Institutions
This is an activity (located on page 131 of the PDF) related to sleep and circadian rhythms as well as space travel.

Why Do Eclipses Happen?
Source Institutions
This fun and simple hands-on astronomy activity lets learners create 3D models of the Earth, Moon and Sun to demonstrate solar and lunar eclipses.

Dunking the Planets
Source Institutions
In this demonstration, learners compare the relative sizes and masses of scale models of the planets as represented by fruits and other foods.

Earth's Energy Cycle: Albedo
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners experiment and observe how the color of materials that cover the Earth affects the amounts of sunlight our planet absorbs.

The Four Seasons
Source Institutions
In this lesson that includes hands-on activities and demonstrations, learners discover that it is the tilt of the Earth's axis (not its proximity to the sun) that causes the seasons.

Make a Sun Clock: Tell Time with the Sun
Source Institutions
Before there were clocks, people used shadows to tell time. In this outdoor activity, learners will discover how to tell time using only a compass, a pencil, a handy printout, and a sunny day.

Egg-cellent Landing
Learners recreate the classic egg-drop experiment with an analogy to the Mars rover landing. The concept of terminal velocity will be introduced, and learners perform several velocity calculations.

Make a Balloon-powered Nanorover
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build a nanorover model using styrofoam meat trays and a balloon.

Morning Star and Evening Star
Source Institutions
This demonstration activity models how Venus appears from Earth.

Jiggly Jupiter
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build edible models of Jupiter and Earth to compare their sizes and illustrate the planets' internal layers.

Space Stations: Follow the Bouncing Ball!
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners predict whether a ball on Earth or a ball on the Moon bounces higher when dropped and why.

Zero-Energy Housing
In this activity, learners investigate passive solar building design with a focus solely on heating.
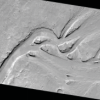
Mars from Above: Carving Channels
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create channel features with flowing water, comparing their observations to real images of Mars and Earth taken by satellites/orbiters.

Weather Stations: Temperature and Pressure
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover the relationship between temperature and pressure in the lower atmospheres of Jupiter and Earth.

Vanishing Craters
Source Institutions
In this activity (on pages 12-15), learners make a crater model and test the effects of weather (rain) on its surface.

Space Rocks!: A Meteorite Game
Source Institutions
In this board game, learners explore the origins of meteors, meteoroids, and meteorites as well as the their characteristics and importance. They also discover some misconceptions about meteors.

Future Moon: The Footsteps of Explorers
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners drop impactors onto layers of graham crackers!

Infant Moon: Moon Mix!
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate the Moon's infancy and model how an ocean of molten rock (magma) helped shape the Moon that we see today.
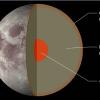
Recipe for a Moon
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover that the Moon, like Earth, is made up of layers of different materials. Learners work in teams to make models of the interiors of the Moon and Earth.
