Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 46

Altered Reality
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover that the human brain is highly adaptable. Learners try to toss beanbags at a target while wearing prism goggles.

Colors, Colors?
Source Institutions
In this activity related to the famous "Stroop Effect," learners explore how words influence what we see and how the brain handles "mixed messages." Learners read colored words and are asked to say th
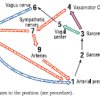
Baroreceptor Reflex Role Play
Source Institutions
In this activity about the baroreceptor reflex (BR) arc (page 123 of the PDF), learners discover the importance of maintaining adequate arterial blood pressure through a role playing exercise.

Experiencing Parallax With Your Thumb
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate parallax, a method used to measure distances to stars and planets in the solar system.
Building a Magic Carpet
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 89 of the PDF), learners compare and contrast pitch and roll motions by using a Magic Carpet maze similar to one that was used for Neurolab investigations about microgravity.

Pitch, Roll and Yaw: The Three Axes of Rotation
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 87 of the PDF), learners move their bodies to better understand the three axes of rotation: pitch, roll and yaw.

Half Full or Half Empty
Source Institutions
In this activity (12th activity on the page), learners conduct an experiment to demonstrate how muscles are constantly feeding information to the brain about what they are doing.

Measuring Your Breathing Frequency at Rest
Source Institutions
In this activity about the brain and sleep (on page 138 of the PDF), learners measure their resting breathing rates. Learners will discover that breathing frequencies vary amongst individuals.

Spinning Illusions
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners construct three optical illusion toys to examine how our brains play tricks on what we see.
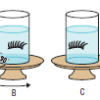
Visualizing How the Vestibular System Works
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 59 of the PDF), learners spin and observe false eyelashes in jars of water (prepared at least 1 day ahead of time) to investigate the effects of different types of motion on the
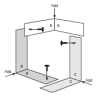
Building a 3-D Space Maze: Escher Staircase
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 95 of the PDF), learners create Escher Staircase models similar to those that were used by Neurolab's Spatial Orientation Team to investigate the processing of information about

Molecule Match
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will use their nose to sniff out hidden scents using extracts and cotton balls. Activity includes materials list, game instructions, STEM connections and more.

Changing Body Positions: How Does the Circulatory System Adjust?
Source Institutions
In this activity about how the body regulates blood pressure (page 117 of the PDF), learners make and compare measurements of heart rate and blood pressure from three body positions: sitting, standing
Our Sense of Sight: Eye Anatomy and Function
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate the sense of sight and develop and conduct their own experiments.

Circles or Ovals?
Source Institutions
This science activity demonstrates the dominant eye phenomena. What does your brain do when it sees two images that conflict?

Our Sense of Sight: Color Vision
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate color vision as well as plan and conduct their own experiments.

Shrinking Spot
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners control the (apparent) size of a hole with their brain.
Smell Detective
Source Institutions
In this activity about olfaction (8th activity on the page), learners smell 10 different items with different odors. Then they try to identify the smells when they are mixed together.

Seeing 3D
Source Institutions
Create 3D glasses and use them to explore color, light and optics. Fool your brain into 'seeing' three dimensions on a flat surface!
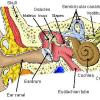
Model Eardrum
Source Institutions
In this activity (last activity on the page), learners make a model of the eardrum (also called the "tympanic membrane") and see how sound travels through the air.
