Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 20
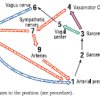
Baroreceptor Reflex Role Play
Source Institutions
In this activity about the baroreceptor reflex (BR) arc (page 123 of the PDF), learners discover the importance of maintaining adequate arterial blood pressure through a role playing exercise.

Pitch, Roll and Yaw: The Three Axes of Rotation
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 87 of the PDF), learners move their bodies to better understand the three axes of rotation: pitch, roll and yaw.

Our Sense of Touch: Two-Point Discrimination
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate the touch sensory system and discover how to plan and carry out their own experiments.

Measuring Your Breathing Frequency at Rest
Source Institutions
In this activity about the brain and sleep (on page 138 of the PDF), learners measure their resting breathing rates. Learners will discover that breathing frequencies vary amongst individuals.
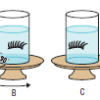
Visualizing How the Vestibular System Works
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 59 of the PDF), learners spin and observe false eyelashes in jars of water (prepared at least 1 day ahead of time) to investigate the effects of different types of motion on the
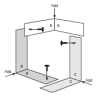
Building a 3-D Space Maze: Escher Staircase
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 95 of the PDF), learners create Escher Staircase models similar to those that were used by Neurolab's Spatial Orientation Team to investigate the processing of information about

Our Sense of Sight: Color Vision
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate color vision as well as plan and conduct their own experiments.
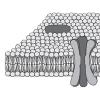
Build-A-Membrane
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners cut, fold, and paste paper representing biomolecules to create a three-dimensional cell membrane with embedded proteins.
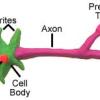
The Model Neuron
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create a model of a neuron by using colored clay or play dough. Learners use diagrams to build the model and then label the parts on a piece of paper.
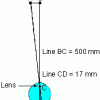
Measuring Your Blind Spot
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners calculate the width (horizontal diameter) of the blind spot on their retina. Learners make a blind spot tester using a piece of notebook paper.
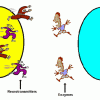
Synaptic Tag
Source Institutions
In this outdoor activity, learners review the parts of the synapse and their functions by playing a game.
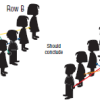
Target Recognition and Synapse Formation During Development
Source Institutions
In this activity about neuron/target muscle recognition (page 44 of the PDF), learners arranged in two rows facing away from each other use string to simulate neural development.

No Saliva, No Taste?
Source Institutions
In this activity (4th activity on the page), learners test to see if saliva is necessary for food to have taste.
Neuron Chain Tag
Source Institutions
In this outdoor activity, learners play a game of Tag to discover how neurons attach themselves to each other to form a chain.

Jumpin' the Gap
Source Institutions
In this simulation of synapses, learners act out communication at the neural level by behaving as pre-synaptic vesicles, neurotransmitters, post-synaptic receptors, secondary messengers and re-uptake

Seeing in the Dark
Source Institutions
In this activity (17th on the page), learners investigate why you cannot see colors in dim light.

What Cells Can I See in Muscle and Spinal Cord Tissues?
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 37 of the PDF), learners observe, on a prepared slide, muscle and spinal cord cells from a rat.

Raising the Level of Carbon Dioxide in Your Blood
Source Institutions
In this activity (on page 146 of the PDF), learners will explore the effects of increased carbon dioxide in the bloodstream.

Introduction to the Scientific Method
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 26 of the PDF), learners make observations, formulate hypotheses and design a controlled experiment, based on the reaction of carbon dioxide with calcium hydroxide.

How Long Can You Hold Your Breath?
Source Institutions
In this activity (on page 142 of the PDF), learners will compare breathing rates before and after hyperventilation to explore how reduced carbon dioxide levels in the blood lower the need to breathe.
