Search Results
Showing results 21 to 40 of 55

Circles or Ovals?
Source Institutions
This science activity demonstrates the dominant eye phenomena. What does your brain do when it sees two images that conflict?

Squirming Palm
Source Institutions
Known as the waterfall effect, this activity demonstrates adaptation in our visual system.

Persistence of Vision
Source Institutions
If you had a long tube with a 5 millimeter wide slit, would you see the entire Golden Gate Bridge?

Tactile Mazes
Source Institutions
In this activity (15th activity on the page) about the sense of touch, learners use glue and cardboard to construct a maze they use with their eyes closed.

Thread the Needle: Using Two Eyes Gives You Depth Perception
Source Institutions
Closing one eye eliminates one of the clues that your brain uses to judge depth. Trying to perform a simple task with one eye closed demonstrates how much you rely on your depth perception.

Taste Match Game
Source Institutions
In this activity (3rd activity on the page), learners taste test different foods and categorize them as sweet, bitter, sour, or salty. Learners compare their results with the group.

Touch Boards
Source Institutions
Use this activity (13th activity on the page) to introduce learners to the sense of touch. Learners collect objects of varying textures like feathers, rocks, sand, etc.

Seeing 3D
Source Institutions
Create 3D glasses and use them to explore color, light and optics. Fool your brain into 'seeing' three dimensions on a flat surface!

Mystery Noises
Source Institutions
In this game (4th activity on the page) about hearing, learners test their ability to identify various sounds without looking.
Expose Your Nose
Source Institutions
In this simple exploratory activity (1st activity on the page), blindfolded learners try to identify mystery items by smell.

Memory Solitaire
Source Institutions
In this online game, learners practice memory recall. They are shown a collage of pictures for two minutes, then have to write down everything they remember and check how they did.

Shifting Backgrounds, Shifting Images
Source Institutions
In this quick activity/demonstration (5th on the page), learners explore depth perception.
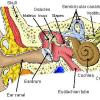
Model Eardrum
Source Institutions
In this activity (last activity on the page), learners make a model of the eardrum (also called the "tympanic membrane") and see how sound travels through the air.
Smell Match
Source Institutions
In this matching activity (3rd activity on the page), learners use their sense of smell to match pairs of opaque containers filled with various smelly items like orange peel, roses, or moth balls.

Thaumatropes
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will make a thaumatrope, an old-fashioned optical illusion that dates back to the 1820s.

Reaction Time
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct an experiment to test how fast they can react. Learners try to catch a piece of paper with a ruler printed on it (or a ruler) as quickly as they can.

Two Ears are Better Than One: Sound Localization
Source Institutions
This activity (9th activity on the page) about hearing demonstrates to learners the importance of having two ears.

Sand Paper Rankings
Source Institutions
In this activity (2nd activity on the page), learners explore the sensitivity of their sense of touch.

Tactile Double Trouble
Source Institutions
In this activity (11th activity on the page), learners use their sense of touch to identify matching pairs of objects hidden in bags. Learners can also play this game with partners.

The Nose Knows
Source Institutions
In this activity (2nd activity on the page), learners explore how the nose is responsible for part of the flavor we taste in food.
