Search Results
Showing results 81 to 100 of 233

Water Sphere Lens
Source Institutions
In this activity about light and refraction, learners make a lens and magnifying glass by filling a bowl with water.
All Mixed Up!: Separating Mixtures
Source Institutions
Visitors separate a mixture of pebbles, salt crystals, and wood shavings by adding water and pouring the mixture through a strainer.

The Self-Watering Terrarium
Source Institutions
In this biology/ecology activity, learners construct a terrarium out of a tennis ball container. This terrarium is unique because it never has to be watered.
Crumple a Watershed
Source Institutions
Learners gain an intuitive knowledge of the physical aspects of watersheds by creating their own watershed models.

See It to Believe It: Visual Discrimination
Source Institutions
In this activity (12th on the page), learners investigate their ability to discriminate (see) different colors.

Identifying Erosion
Source Institutions
In this environmental science activity (page 3 of the PDF), leaners will identify and explain the causes of erosion.
Hot and Cold: Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions
Source Institutions
Visitors mix urea with water in one flask and mix calcium chloride with water in another flask. They observe that the urea flask gets cold and the calcium chloride flask gets hot.
Close, Closer, Closest
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners perform an experiment that models a chromatography-like process called electrophoresis, a process used to analyze DNA.
DNA Extraction: Look at your genes!
Source Institutions
Extract your DNA from your very own cells! First, learners swish salt water in their mouth to collect cheek cells and spit the water into a glass.
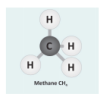
Let's Make Molecules
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use gumdrops and toothpicks to model the composition and molecular structure of three greenhouse gases: carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor (H2O) and methane (CH4).

What Lives Here
Source Institutions
In this outdoor activity/field trip, learners explore an aquatic site such as a pond, lake, stream, river or seashore to find and investigate plants and animals that live in water.
What Does Life Need to Live?
Source Institutions
In this astrobiology activity (on page 11 of the PDF), learners consider what organisms need in order to live (water, nutrients, and energy).

Plant Power
Source Institutions
In this chemistry challenge, learners identify which plants have the enzyme "catalase" that breaks hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen.
Weighty Questions
Source Institutions
In this activity about humans and space travel (page 1 of PDF), learners compare and contrast the behavior of a water-filled plastic bag, both outside and inside of a container of water.

Lotus Leaf Effect
Source Institutions
This is a demonstration about how nature inspires nanotechnology. It is easily adapted into a hands-on activity for an individual or groups.

Dip Dip, Hooray
Source Institutions
Lakes, streams and other freshwater bodies are a habitat for lots of living things, big and small.

Single-Cell Life
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create a soil and water model of a single-cell life environment and study living microorganisms.

Challenge: Microgravity
Source Institutions
In this activity about the circulatory system and space travel (on page 38 of the PDF), learners use water balloons to simulate the effects of gravity and microgravity on fluid distribution in the bod

Make a Lake
Source Institutions
Where rainwater goes after the rain stops? And why there are rivers and lakes in some parts of the land but not in others?

Half Full or Half Empty
Source Institutions
In this activity (12th activity on the page), learners conduct an experiment to demonstrate how muscles are constantly feeding information to the brain about what they are doing.
