Search Results
Showing results 21 to 40 of 71

What's in the Water?: Biotic and Abiotic Elements in Aquatic Ecosystems
Source Institutions
In this investigation learners explore the differences between, and interdependence of, living and nonliving elements in a water ecosystem.

Erosion and Floods
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create models of erosion and floods and learn to recognize both in their environment.

Moisture Makers
Source Institutions
In this outdoor activity, learners compare the moisture released from different kinds of leaves and from different parts of the same leaf, by observing the color change of cobalt chloride paper.

Wonderful Weather
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct three experiments to examine temperature, the different stages of the water cycle, and how convection creates wind.

OBIS Oil Spill
Source Institutions
In this outdoor activity, learners simulate an oil spill using popcorn (both oil and popcorn float on water), and estimate the spill's impact on the environment.
Investigating Density Currents
Source Institutions
In this lab activity, learners explore how to initiate a density current. Learners measure six flasks with different concentrations of salt and water (colored blue).

Oh Buoy!
Source Institutions
Learners work in pairs to design, construct, and test a device that exhibits positive, neutral, and negative buoyancy. They test a number of different objects in water to see if they sink or float.
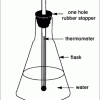
Using Solar Energy
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover how solar energy can be used to heat water.

Boats Afloat
Source Institutions
In this water activity, learners build boats that float and sink. First, learners listen to the book, "Who Sank the Boat" and practice making predictions throughout the story.

The Ability of Permeability
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 11 of the PDF), learners investigate how quickly water moves through various materials. They measure and compare the permeability of gravel, sand, and soil.

Indicating Electrolysis
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build a simple electrolysis device. Then learners use an indicating solution to visualize hydrogen and oxygen molecules in water.

Runaway Runoff
Source Institutions
When it rains, water can collect on top of and seep into the ground. Water can also run downhill, carrying soil and pollution with it.

Catch a Wave: How Waves are Formed
Source Institutions
In this three-part activity, learners explore how waves are formed and why some waves are bigger than others. First, learners observe waves of water in a pan generated by an electric fan.

Energetic Water
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how hot and cold water move. Learners observe that temperature and density affect how liquids rise and fall.
Crumple a Watershed
Source Institutions
Learners gain an intuitive knowledge of the physical aspects of watersheds by creating their own watershed models.

Portable Potable Pressure
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use plastic water bottles, wood, and water to build an inexpensive and portable tool to demonstrate one atmosphere of pressure at sea level.
Build A Hydrometer
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will explore how a hydrometer works by building a working model and conducting experiments.
Weighty Questions
Source Institutions
In this activity about humans and space travel (page 1 of PDF), learners compare and contrast the behavior of a water-filled plastic bag, both outside and inside of a container of water.
Investigating Convection
Source Institutions
This experiment is designed to illustrate how fluids, including water, have the ability to flow.

Challenge: Microgravity
Source Institutions
In this activity about the circulatory system and space travel (on page 38 of the PDF), learners use water balloons to simulate the effects of gravity and microgravity on fluid distribution in the bod
