Search Results
Showing results 21 to 40 of 47
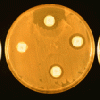
Chemical Methods of Control
Source Institutions
In this lab, learners evaluate the relative effectiveness of various chemical substances (i.e. garlic powder, bathroom cleaner, mouthwash, etc.) as antimicrobial agents.

Paleontologists: Can You Dig It?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore the work of paleontologists.

Logs to Soil
Source Institutions
In this outdoor activity, learners cut through and investigate rotten logs and then make log-profile puzzles for each other.

Litter Critters
Source Institutions
In this outdoor activity, learners use a "litter-critter" wheel to help them identify different animals they find living in a natural litter habitat.

Styrofoam Traps
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use Styrofoam to collect organisms from a pond, estuary or marine environment and then examine what they have caught with a microscope.

Coverslip Traps
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use coverslips to collect organisms from a pond, estuary or marine environment and then examine what they have caught with a microscope.
Candy Chemosynthesis
Source Institutions
In this activity, groups of learners work together to create edible models of chemicals involved in autotrophic nutrition.

Testing Antimicrobials:: Antibacterial Soap? Do They All Work the Same?
Source Institutions
Many common household cleaners are antimicrobials.

Comparing Sizes of Microorganisms
Source Institutions
In this activity related to microbes, learners create scale models of microorganisms and compare relative sizes of common bacteria, viruses, fungi and protozoa using metric measures: meters, centimete

Microbes are Everywhere
Source Institutions
In this four-day activity, learners grow bacteria and/or fungi from a variety of locations and compare the results.

What Do You Know About Microbes?
Source Institutions
This is a series of quick activities/demos and pre-assessment tools that evaluate learners' current understanding of microbes and introduce them to basic information about microbes.
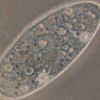
Biological Succession in a Microecosystem
Source Institutions
This laboratory activity helps learners understand the concept of biological succession by simulating the process in a microenvironment with various protozoans.

Bacteriopolis
Source Institutions
In this long-term activity, learners make a home for a colorful community of microorganisms.
Hot Potato
Source Institutions
In this health activity (page 7 of the PDF), learners will discover the importance of handwashing as a factor in reducing the spread of pathogens.

Life Size: What's in a microbe?
Source Institutions
In this activity on page 3 of the PDF, learners visualize the relative size and structural differences between microbes that have the potential to cause disease.

Wild Sourdough
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore chemistry and the microbial world by making their own sourdough starter and bread at home using only flour and water.
Balloon Bugs
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make balloon models of disease-causing bacteria.

Demonstrating An Epidemic
Source Institutions
This experiment allows learners to experience a small scale "epidemic," demonstrating the ease with which disease organisms are spread, and enables learners to determine the originator of the "epidemi
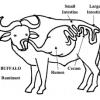
Ruminating on the Digestive System
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will review the functions of basic digestive organs, understand how diet affects digestion, understand how digestive tracks may differ, and then step outside to compare the

Handwashing Laboratory Activities: Bowl Technique
Source Institutions
In this lab (Activity #2 on page), learners compare bacteria growth on two petri dishes containing nutrient agar. Learners touch the doors, faucets, etc.
