Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 24

Changing the Density of a Liquid: Adding Salt
Source Institutions
Learners see that a carrot slice sinks in fresh water and floats in saltwater.

Separation Anxiety
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover the primary physical properties used to separate pure substances from mixtures.

Comparing the Density of an Object to the Density of Water
Source Institutions
Learners compare the weight of equal volumes of wax, water, and clay. Learners discover that since the wax weighs less than an equal volume of water, it is less dense than water and will float.
Atoms and Matter (3-6)
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build models of atoms and molecules, then consider their role in different phases of matter, density, and mixtures and solutions.

Changing the Density of an Object: Changing Shape
Source Institutions
Learners will see that changing the shape of an object, like a clay ball, that is more dense than water, can affect whether the object will sink or float.

Exploring How Liquids Behave
Source Institutions
Learners apply their knowledge from a previous study to identify different liquids--water, corn syrup, and vegetable oil.

Oil Spill Cleanup
This hands-on experiment will provide learners with an understanding of the issues that surround environmental cleanup.
Submersibles and Marshmallows
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover the difficulty of ocean exploration by human beings as they investigate water pressure.
Buoyancy Bulls-Eye
Source Institutions
In this hands-on activity, learners will construct a scuba diver that can float in order to explore how sea creatures stay neutrally buoyant in the ocean and to see what kinds of forces might be influ

Using Color to See How Liquids Combine
Source Institutions
Learners add different liquids (water, salt water, alcohol, and detergent solution) to water and observe the different ways the different liquids combine with water.

What's So Special about Water: Solubility and Density
Source Institutions
In this activity about water solubility and density, learners use critical thinking skills to determine why water can dissolve some things and not others.

Weather Stations: Winds
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use a toaster to generate wind and compare the appliance's heat source to Jupiter's own hot interior. Learners discover that convection drives wind on Jupiter and on Earth.

Changing the Density of a Liquid: Heating and Cooling
Source Institutions
Learners investigate how the temperature of water affects its density.

Changing the Density of an Object: Adding Material
Source Institutions
Learners see that a can of regular cola sinks while a can of diet cola floats. As a demonstration, bubble wrap is taped to the can of regular cola to make it float.
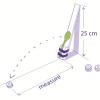
Volcanic Material Catapult Investigation
Source Institutions
This activity (located on page 3 of the PDF under GPS: Lava Flow Activity) is a full inquiry investigation into the relationship between an object’s mass and the distance it is thrown by a catapult.

Eyedropper Hydrometer: Buoy your understanding of density
Source Institutions
Build a hydrometer (measures the density of a liquid) using a pipet or eyedropper.

Boats Afloat
Source Institutions
In this water activity, learners build boats that float and sink. First, learners listen to the book, "Who Sank the Boat" and practice making predictions throughout the story.

Sink It
Source Institutions
Learners classify a variety of objects by their characteristics. They then design an experiment to determine which objects float or sink in water and add this characteristic to their classification.

Convection Demonstration
Source Institutions
In this quick activity (located on page 2 of the PDF under GPS: Balloon Fiesta Activity), learners will see the effects of convection and understand what makes hot air balloons rise.

Float Your Boat
Source Institutions
In this physics activity, learners will explore buoyancy.
