Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 21

In the Middle
Source Institutions
In this game-like activity (5th activity on the page), learners explore their auditory acuity as well as the importance of having two ears.
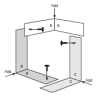
Building a 3-D Space Maze: Escher Staircase
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 95 of the PDF), learners create Escher Staircase models similar to those that were used by Neurolab's Spatial Orientation Team to investigate the processing of information about

Pitch, Roll and Yaw: The Three Axes of Rotation
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 87 of the PDF), learners move their bodies to better understand the three axes of rotation: pitch, roll and yaw.
The Ups and Downs of Body Temperature
Source Institutions
In this activity (1st on the page), learners explore circadian rhythms by keeping track of their body temperature.
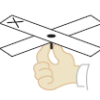
Building a Magic Carpet
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 89 of the PDF), learners compare and contrast pitch and roll motions by using a Magic Carpet maze similar to one that was used for Neurolab investigations about microgravity.

Half Full or Half Empty
Source Institutions
In this activity (12th activity on the page), learners conduct an experiment to demonstrate how muscles are constantly feeding information to the brain about what they are doing.

No Saliva, No Taste?
Source Institutions
In this activity (4th activity on the page), learners test to see if saliva is necessary for food to have taste.

Color Spy
Source Institutions
In this activity (16th on the page), learners play a variation of the "I Spy" game to explore color. Learners work in teams with each team assigned a color.

Benham's Disk
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make a Benham Top to explore visual illusions and optics.

Auditory Acuity
Source Institutions
This activity (8th activity on the page) tests learners' ability to identify things using only the sense of hearing.

How Fast Are You?
Source Institutions
This activity is designed to let learners measure their reaction time or response time to something they see.

Colors, Colors?
Source Institutions
In this activity related to the famous "Stroop Effect," learners explore how words influence what we see and how the brain handles "mixed messages." Learners read colored words and are asked to say th
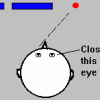
The Blind Spot
Source Institutions
In this activity (1st on the page), learners find their blind spot--the area on the retina without receptors that respond to light.

Dark Adaptation
Source Institutions
In this activity (6th on the page), learners investigate how photoreceptors in the eye (rods and cones) "adapt" to low light conditions.

Mystery Noises
Source Institutions
In this game (4th activity on the page) about hearing, learners test their ability to identify various sounds without looking.

Depth Perception
Source Institutions
In this easy demonstration (3rd on the page), learners explore depth perception by conducting a test with two pencils.

The Senses of "Unknown Creatures"
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use earthworms as "unknown creatures" from the South American jungle to find out how animals use senses.

A Penny Saved is a Penny Heard
Source Institutions
In this activity (11th activity on the page), learners use pennies to test their hearing acuity.

Seeing in the Dark
Source Institutions
In this activity (17th on the page), learners investigate why you cannot see colors in dim light.

Accommodating Accommodation
Source Institutions
In this demonstration (18th on the page), learners conduct a simple test to explore how the cornea refracts light, which is further bent by the eye lens through a process known as accommodation.
