Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 33

Matter on the Move
Source Institutions
Learners observe and conduct experiments demonstrating the different properties of hot and cold materials.

Look-alike Liquids
Source Institutions
Learners add drops of four liquids (water, alcohol, salt water, and detergent solution) to different surfaces and observe the liquids' behavior.
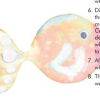
Universal Indicator Rainbow Trout
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners cut out a fish and then "paint" it using universal indicator and acids and bases.

Changing the Density of a Liquid: Adding Salt
Source Institutions
Learners see that a carrot slice sinks in fresh water and floats in saltwater.

M&M's in Different Temperatures
Source Institutions
Learners design their own experiment to investigate whether the temperature of the surrounding water affects the rate at which the colored coating dissolves from an M&M.

Comparing the Density of an Object to the Density of Water
Source Institutions
Learners compare the weight of equal volumes of wax, water, and clay. Learners discover that since the wax weighs less than an equal volume of water, it is less dense than water and will float.

Formation of a Precipitate
Source Institutions
Learners create hard water by mixing Epsom salt and water. Then they compare what happens when soap solution is mixed with hard water and regular water.

Changing the Density of an Object: Changing Shape
Source Institutions
Learners will see that changing the shape of an object, like a clay ball, that is more dense than water, can affect whether the object will sink or float.

Mystery Powders
Source Institutions
In this activity on page 2 of the PDF (Get Cooking With Chemistry), learners conduct chemical tests on certain powders used in cooking.

Evaporation
Source Institutions
This three-part activity consists of an activity that groups of learners develop themselves, a given procedure, and an optional demonstration.

Crushing Test
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners design a crushing test and discover that identifying and controlling the variables may be difficult.
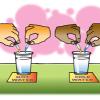
Molecules in Motion
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners add food coloring to hot and cold water to see whether heating or cooling affects the speed of water molecules.

Neutralizing Acids and Bases
Source Institutions
Learners use their knowledge of color changes with red cabbage indicator to neutralize an acidic solution with a base and then neutralize a basic solution with an acid.

Color Changes with Acids and Bases
Source Institutions
Learners mix a variety of substances with red cabbage juice. The juice changes color to indicate whether each substance is an acid or a base.

Polishing Pennies
Source Institutions
In this experiment, learners try different liquids to see which ones clean pennies best. Liquids to try include water, lemon juice, cola, vinegar, and dishwashing detergent.

Racing M&M Colors
Source Institutions
Learners design their own experiment to determine which M&M color dissolves the fastest in water.

Exploring Moisture on the Outside of a Cold Cup
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore the relationship between cooling water vapor and condensation. Learners investigate condensation forming on the outside of a cold cup.

Secret Goldenrod Messages
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners write invisible messages on goldenrod paper, and make the message appear and disappear using acids and bases.

M&M's in Different Sugar Solutions
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate whether having sugar already dissolved in water affects the speed of dissolving and the movement of sugar and color through the water.
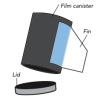
Pop Rockets
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make film canister rocket ships. A fin pattern is glued onto the outside of the canister, and fuel (water and half an antacid tablet) is mixed inside the canister.
