Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 30

Lava Layering: Making and Mapping a Volcano
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover how geologists use stratigraphy, the study of layered rock, to understand the sequence of geological events.

Excavating and Mapping Under Water
Source Institutions
In this archaeology activity, learners consider ways in which excavating an underwater site is different from excavating a terrestrial site.

Do Your Own Dig
Source Institutions
In this outdoor archaeology activity, learners use mathematical skills and scientific inquiry to generate and process information from their own excavation site.

Trees: Recorders of Climate Change
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners are introduced to tree rings by examining a cross section of a tree, also known as a “tree cookie.” They discover how tree age can be determined by studying the rings and ho
Air-filled (Pneumatic) Bone Experiments
Source Institutions
Just like birds, some dinosaurs had air-filled (pneumatic) bones, which made the dinosaurs' skeletons lighter.

Collect Invertebrates to Determine Water Quality
Source Institutions
This activity (located on page 3 of the PDF under GPS: Alligator Habitat Activity) is a full inquiry investigation into organisms and the health of their ecosystems.
What Does Life Need to Live?
Source Institutions
In this astrobiology activity (on page 11 of the PDF), learners consider what organisms need in order to live (water, nutrients, and energy).

Dinosaur Breath
Through discussion and hands-on experimentation, learners examine the geological (ancient) carbon cycle.

Environmental Chemistry
Source Institutions
In this activity with several mini experiments, learners explore the chemistry that helps scientists learn about the environment and how they can help save it.
Signs of Change: Studying Tree Rings
Source Institutions
In this very hands-on lesson, learners will investigate dendrochronology (the study of tree rings to answer ecological questions about the recent past) and come up with conclusions as to what possible

Size, Scale and Models
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners take measurements and create charts to learn about the size of dinosaurs and their relative scale to humans.

Treasures in the Rough
Source Institutions
In this archaeology activity, learners make observations and conduct an experiment to demonstrate the effect saltwater has on artifacts.

Super Soaker
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 1 of the PDF under SciGirls Activity: Bogs), learners will test cups full of potting soil, sand, and sphagnum moss to see which earth material is able to soak up the most water.
Weathering and Erosion
Source Institutions
In this multi-station lab, learners conduct a series of experiments to explore the processes and effects of weathering and erosion.

Make a Terrarium
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make a miniature greenhouse or "terrarium" to explore the greenhouse effect.

Super Soaking Materials
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will test cups full of potting soil, sand, and sphagnum moss to see which earth material is able to soak up the most water.
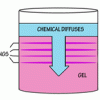
Liesegang Rings
Source Institutions
This display shows slow chemical reactions in colorful crystal formations known as Liesegang Rings. These reactions are similar to those forming the rings in agates.

Bury Me Not!
Source Institutions
This activity (page 2 of the PDF under SciGirls Activity: Bogs) is a full inquiry investigation into decomposition.

Sand Dunes
Source Institutions
This outdoor activity (on page 2 of the PDF under SciGirls Activity: Sand Dunes) is a full inquiry investigation into how the amount of moisture in a sand dune relates to the number of plants growing

Rock Bottoms
Source Institutions
Learners add acid rain (nitric acid) to two cups that represent lakes. One cup contains limestone gravel and the other contains granite gravel.
