Search Results
Showing results 1 to 16 of 16

Programming Languages: Marching Orders
Source Institutions
In this activity about computer programming, learners follow instructions in a variety of ways in order to successfully draw figures.
Tourist Town: Dominating Sets
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use a fictitious map of "Tourist Town" and counters to problem solve how to place ice-cream vans on street intersections so that every other intersection is connected to one
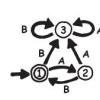
Treasure Hunt: Finite-State Automata
In this computer science activity about finite-state automaton (on page 45 of the PDF), learners use a map and choose various pathways to find Treasure Island.

Beat the Clock: Sorting Networks
Source Institutions
Even fast computers are limited to how quickly they can solve problems. One way to speed things up is to use several computers at once.
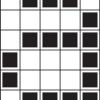
Color by Numbers: Image Representation
Source Institutions
Computers store drawings, photographs, and other pictures using only numbers. Through this activity, learners decode numbers to create pictures using the same process that computers use.

Count the Dots: Binary Numbers
Source Institutions
Data in computers is stored and transmitted as a series of zeros and ones. Learners explore how to represent numbers using just these two symbols, through a binary system of cards.

Pico Cricket Compass
Source Institutions
Learners can program a compass to draw a circle by itself using a Pico Cricket, some Legos, and lots of tape! Pico Cricket is required.

Computation and Estimation: Roll Out The Barrel
Source Institutions
In this math lesson, learners apply mathematical modeling to solve a real-world storage problem, in which a manufacturing company is given two options for storing oil barrels.
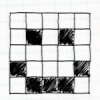
Passion for Pixels
Source Institutions
In this technology activity, learners explore digital imaging and pixels. Learners "transmit" an image to a partner by creating an image on grid paper.
Lightest and Heaviest: Sorting Algorithms
Source Institutions
Computers are often used to put lists into some sort of order—for example, names into alphabetical order, appointments or e-mail by date, or items in numerical order.

The Orange Game: Routing and Deadlock in Networks
Source Institutions
When a lot of people share one network (such as cars using roads, or messages getting through the Internet), there is the possibility that competing processes will create a “deadlock," or an interrupt

Multitasking Mania
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct scientific research on multitasking. Learners determine if multitasking with media while doing homework affects their ability to successfully complete the homework.

Computation and Estimation: Alphabits
Source Institutions
In this math lesson, learners apply the concepts of ratios and percentages to the distribution of letters contained in a box of Alphabits® cereal.

Aerial Imagery
Source Institutions
This activity (on page 2 of the PDF under SciGirls Activity: Earthquakes) is a full inquiry investigation into aerial imagery.

Coral Snapshots: Biodiversity in Marine Protected Areas
Source Institutions
In this data activity, learners analyze data from coral reef snapshots taken by scientists at the Virginia Institute of Marine Science.

Algebra: Aw Chute!
Source Institutions
In this math lesson, learners determine and compare the rate of descent of various learner-constructed parachutes. Learners construct parachutes that will have maximum hang times.
