Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 40

Jay Play
Source Institutions
In this outdoor activity, learners find out the color of food that jays prefer and then try to change the birds' preference by altering the taste of the food with salt.

Food Grab
Source Institutions
In this outdoor activity, learners design devices that will catch prey or gather plants.

Otter Smorgasbord
Source Institutions
In this graphing activity (on pages 33-40), learners investigate how much and what kinds of food sea otter pups eat during their first year of life.

Food Webs
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners construct possible food webs for six different ecosystems as they learn about the roles of different kinds of living organisms.

Grabbing a Bite to Eat
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners perform an experiment that replicates the dilemma faced by birds in acquiring food from a confined area.

For the Birds
Source Institutions
In this outdoor activity, learners turn the fun of feeding wild birds into an investigation of bird behavior.

Flocking for Food
Source Institutions
In this outdoor beach activity, learners use a variety of "beaks" (such as trowels, spoons or sticks) to hunt for organisms that shore birds might eat.

Biotechnology Through Time
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate the history and development of agricultural biotechnology.

Clipbirds
Source Institutions
In this simulation of natural selection, learners use binder clips in three different sizes to represent the diversity of beak sizes in a bird population.

Population Game
Source Institutions
In this outdoor game, learners simulate a herd of deer trying to survive in an area called the "home range." Learners explore the concept of "carrying capacity"—what size population of an organism can

Sustainable Grazing
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate the food, water, and space needs of common livestock animals.

Make a "Mummy"
Source Institutions
The Ancient Egyptians used a naturally-occurring salt from the banks of the Nile River, called natron, to mummify their dead.

Junk-in-the-Box
Source Institutions
In this outdoor activity, learners explore how a surprising number of animals use human-made litter, such as cans and crumpled paper, to find food and shelter in their environment.

Animal Scent
Source Institutions
This activity (on page 3 of the PDF under GPS: Animal Scent Activity) is a full inquiry investigation into animal behavior.
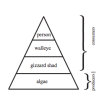
Who Can Harvest a Walleye?
Source Institutions
This activity focuses on interactions within Earth systems and the effects of human activities. In this activity learners build a biomass pyramid.

Frog Eggs
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners compare frog eggs to chicken eggs to better understand why frog eggs need water. Learners compare a boiled chicken egg to "frog eggs" represented by boiled tapioca.

Shape Up!
Source Institutions
In this activity (25th on the page) about learning and memory, learners explore a training method that animal trainers employ called "shaping." Working in pairs, learners will attempt to "shape" each
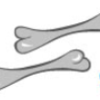
Air-filled (Pneumatic) Bone Experiments
Source Institutions
Just like birds, some dinosaurs had air-filled (pneumatic) bones, which made the dinosaurs' skeletons lighter.
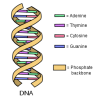
Close, Closer, Closest
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners perform an experiment that models a chromatography-like process called electrophoresis, a process used to analyze DNA.

What's in the Water?: Biotic and Abiotic Elements in Aquatic Ecosystems
Source Institutions
In this investigation learners explore the differences between, and interdependence of, living and nonliving elements in a water ecosystem.
