Search Results
Showing results 21 to 40 of 63
Liquid Crystals Interact with Light!
Source Institutions
In this two-part activity, learners explore the properties of liquid crystals, which are responsible for why mood rings change color.
Globe at Night
Source Institutions
In this international citizen science activity, learners measure their night sky brightness and submit their observations into an online database.
Planet Surfing
Source Institutions
In this astronomy activity (page 6 of the PDF), learners will compare and contrast two planets in the solar system using data obtained from the internet.
Lagging Sound
Source Institutions
In this group activity, learners see and hear the speed of sound. A learner designated the "gonger" hits a gong, once every second, as the rest of the group watches and listens from a distance.
Pupil to Pupil
Source Institutions
In this quick and simple activity about reflexes (at the top of the webpage), learners conduct a simple test to explore pupillary response.
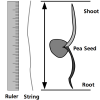
Easy PEAsy Seed Germination
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners determine the necessary conditions for pea seed germination.

Illuminations on Rates of Reactions
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate the speed of chemical reactions with light sticks. Learners discover that reactions can be sped up or slowed down due to temperature changes.

Mirror, Mirror on the Wall: Angles of Reflection
Source Institutions
In this optics activity, learners work in pairs to explore how mirrors work. Learners use tape to mark the angles needed to see each other's reflection in a wall mirror.

Transit Tracks
Source Institutions
In this space science activity, learners explore transits and the conditions when a transit may be seen.
Fish Eyes: More than Meets the Eye
Source Institutions
In this data collection and analysis activity, learners evaluate fish physiology and ecology using vision research data from Dr.

Cylindrical Mirror
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create a cylindrical mirror to see themselves as others see them.
What is Nanotechnology?
Source Institutions
In this activity related to nanotechnology, learners observe some of the effects that result from creating a thin layer of material several nanometers thick.
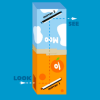
Periscope
Source Institutions
In this optics activity, learners build a spy tool to secretly view things over walls or around corners.
Finding the Size of the Sun and Moon
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build a simple pinhole viewer. They use this apparatus to project images from a variety of light sources, including a candle, the Sun, and the Moon.

Kaleidoscope
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build inexpensive kaleidoscopes using transparency paper and foil (instead of mirrors).

Cardboard Opaque Projector
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners construct a projector out of cardboard to view their favorite images (such as storybook illustrations) on the wall.

Personal Pinhole Theater
Source Institutions
Have you ever heard of a camera without a lens? In this activity, learners create a pinhole camera out of simple materials. They'll see the world in a whole new way: upside down and backwards!
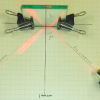
Mirror, Mirror
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners test the Law of Reflection based on experimental evidence. Learners produce raw data and explanations based on their data: pencil tracings of incident and reflection rays.

Telescopes as Time Machines
Source Institutions
This fun, nighttime hands-on astronomy activity lets learners explore how long it takes for light from different objects in the universe to reach Earth.

Count Around
Source Institutions
Learners explore their surroundings while reasoning about categories and counting.
