Search Results
Showing results 81 to 100 of 157
The Right Fit
Source Institutions
In this math activity, learners trace their hands and estimate the number of beans that can fit into their hand tracings. Then, learners glue the beans to the tracing to test out their estimations.

A Swell Activity with Beans
Source Institutions
In this combination chemistry and physics activity, learners explore water absorption in dried beans or peas and learn how this affects their physical properties.
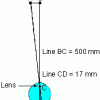
Measuring Your Blind Spot
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners calculate the width (horizontal diameter) of the blind spot on their retina. Learners make a blind spot tester using a piece of notebook paper.

Highway Seismograph
Source Institutions
This is an activity that models the operation of a seismograph, a tool used to measure the size of earthquakes.

Ready, Set, Fizz!
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore the chemical reaction between water and effervescent antacid tablets. This hands-on activity models how a material can act differently when it's nanometer-sized.

Space Jell-O
Source Institutions
Albert Einstein proved that space bends around anything that has mass. This activity uses Jell-O's ability to bend around objects as a model for space bending around planets and stars.

Exploring Measurement
Source Institutions
In this "Sid the Science Kid" activity, learners use their bodies to measure a room. Instead of inches or feet, how many kids does it take to measure the length of a room?

Modeling the Night Sky
Source Institutions
In this two-part activity, learners explore the Earth and Sun's positions in relation to the constellations of the ecliptic with a small model.

Pi Graph
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use a straight line to learn about circles. Learners measure and record the diameter and circumference of different sized cylindrical objects on a chart.

Mapping the Classroom
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover the importance of maps and scale as they work together to create a map of the classroom.

What is a Nanometer?
Source Institutions
This lesson focuses on how to measure at the nanoscale and provides learners with an understanding how small a nanometer really is.

Exploring Tools: Mitten Challenge
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build a LEGO® structure while wearing mittens. This activity shows learners how difficult it is to build small things when your tools are too big.

Size It Up
Source Institutions
In this artistic activity, learners blow up a smaller picture into a larger one, by using a grid.

Exploring Properties: Surface Area
Source Institutions
This hands-on activity demonstrates how a material can act differently when it's nanometer-sized.

Lean, Mean Information Machine: Using a Simple Model to Learn about Chromosomal DNA
Source Institutions
Learners observe a model of a cell and its chromosomal DNA made from a plastic egg and dental floss. Use this model to illustrate how much DNA is held in one cell.

Perspectives: Powers of 10
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners complete a series of drawing activities to explore scale and powers of 10. Learners first trace each other on 1-meter-square pieces of paper.

Meteoroids and the Craters They Make
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate the formation of craters. Learners will examine how the size, angle and speed of a meteorite's impact affects the properties of craters.
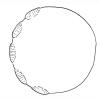
Elephant Foot
Source Institutions
Using a real-size sketch of a baby elephant's footprint, learners estimate, measure and record the width (diameter) and outside edge length (perimeter or circumference) of the footprint.

Mitten Challenge
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners try to put together toy bricks—wearing oven mitts on their hands! This activity shows learners how difficult it is to build small things when your tools are too big.

