Search Results
Showing results 201 to 220 of 532

Cook with a Solar Oven
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make their own solar oven to bake s'mores and learn about how solar energy is absorbed on Earth.

What Does Spit Do?
Source Institutions
Some animals can swallow food whole, but humans have to chew. In this activity, learners will investigate what saliva does chemically to food before we even swallow.

Sweet Measurements
Source Institutions
In this activity on page 3 of the PDF, learners investigate how much sugar is in a soda. Learners use sugar cubes to measure and calculate the amount of sugar in a bottle of soda.
T. rex Cretaceous Treat
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make edible T. rex teeth (with adult assistance). The treat is a white and dark chocolate covered banana on a stick.

A Feast for Yeast
Source Institutions
In this activity on page 6 of the PDF (Get Cooking With Chemistry), learners investigate yeast. Learners prepare an experiment to observe what yeast cells like to eat.

Cool It!
Source Institutions
In this fun hands-on activity, learners use simple materials to investigate evaporation. How can the evaporation of water on a hot day be used to cool an object? Find out the experimental way!

Regolith Formation
Source Institutions
In this three-part activity, learners use food to determine the effects of wind, sandblasting and water on regolith (dust) formation and deposition on Earth.

What's So Special about Water: Solubility and Density
Source Institutions
In this activity about water solubility and density, learners use critical thinking skills to determine why water can dissolve some things and not others.

Mix It Up
Source Institutions
In this math lesson, learners are introduced to proportional reasoning through modeling, sharing, and questioning techniques.

Mixtures and Solutions
Source Institutions
This activity was designed for blind learners, but all types of learners can use it to investigate heterogeneous and homogeneous mixtures and solutions, identify the differences, and explore the conce
Triboluminescence
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover what happens when they crush wintergreen-flavored candies in a very dark room.

Veggies with Vigor
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners try to revive wilted celery. Learners discover that plants wilt when their cells lose water through evaporation. Use this activity to introduce capillary action.

Starch Breakdown
Source Institutions
Learners use Benedict’s solution and heat to test for the presence of simple sugars in glucose, sucrose, starch, and starch combined with amylase.

Dissolving Different Liquids in Water
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners add different liquids to water and apply their working definition of “dissolving” to their observations.

Maritime Munchies
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners follow simple historical maritime recipes to cook up hardtack and swanky, and then compare the foods they eat to what was served on ships in the past.

Avi's Sensational Salt Dough
Source Institutions
In this activity on page 5 of the PDF, learners mimic the process for making bricks. Learners shape and bake creations from a dough that is made from flour, salt, and water.
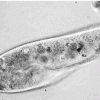
Observing Different Microbes
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use a microscope to examine three different microbes: bacteria, yeast and paramecia. Educator will need to prepare the yeast solution one day before the activity.

The Snack Shop
Source Institutions
In this math activity (Page 11 of the Dining Out! PDF), younger learners count out the total amount of money needed to purchase trail mix using the fewest number of bills/coins possible.

Pickle-oh!: Musical Pickle Instrument
Source Institutions
What's a Pickle-Oh? Two pieces of pickle on a stick are connected to a Pico Cricket (micro controller). When you slide the pickles apart the note changes.

Lighting Up Celery Stalks
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct a series of hands-on experiments that demonstrate how the working of plants' veins, known as capillary action, enables water to travel throughout the length of a pla
