Search Results
Showing results 21 to 40 of 118
Double Dutch Distractions
Source Institutions
This activity (page 2 of the PDF under SciGirls Activity: Double Dutch) is a full inquiry investigation into whether hearing or seeing has a bigger effect on jump rope performance.

Build a Bell Bracelet
Source Institutions
Learners make bell bracelets, place them on their wrists or ankles, and then dance to the rhythms and sounds the bells make. Many cultures use ankle or wrist bells to make music during dancing.

Altered Reality
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover that the human brain is highly adaptable. Learners try to toss beanbags at a target while wearing prism goggles.

Stethoscope
Source Institutions
Make a copy of the first stethoscope with only a cardboard tube! René Laennec invented the first stethoscope in 1819 using an actual paper tube!

Space Stations: Beans in Space
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners perform 20 arm curls with cans that simulate the weight of beans on Earth versus the weights of the same number of beans on the Moon and in space.

The Thousand-Yard Model
Source Institutions
This is a classic exercise for visualizing the scale of the Solar System.

Go with the Flow
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover how hard their hearts work to pump blood.

Tug-of-War
Source Institutions
This activity (on page 2 of the PDF under SciGirls Activity: Tug O' War) is a full inquiry investigation into tug-of-war physics. Groups of learners will test two tug-of-war strategies.

Boomerang
Source Institutions
Everybody loves boomerangs! In this activity about force and motion, the learners will experiment with boomerangs and explore how they work. This is a great activity to get learners up and moving.

Kites
Source Institutions
In this engineering/design activity, learners make a kite, fly it, and then work to improve the design. Learners explore how their kite design variations affect flight.

Water Drop Races
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will explore the physics of liquids and gas by playing with both! Learners of any age use their own breath to move drops of water across a smooth wax paper surface.
Make Your Own Magnus Glider
Source Institutions
Build a glider that uses the same physics as a curve ball, for less than a dime.

Mid-Air Maneuver: Skateboard Science
Source Institutions
To understand how skaters turn in midair, try this little experiment! Individuals can do this activity alone, but it works better with a partner.
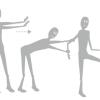
Pathways with Friends
Source Institutions
Directed by instructional cards, learners kinesthetically model cell communication by acting as components in a cell signaling pathway.

Thrown For A Curve: Pitch Like A Big Leaguer
Source Institutions
You may have tried to throw a curveball or a slider, or even a screwball, with an ordinary baseball and found it difficult to do.

Origami Flying Disk
Source Institutions
In this three-part activity, learners use paper to explore Bernoulli's Principle — fast-moving air has lower pressure than non-moving air.

Buoyant Bubbles
Source Institutions
What keeps bubbles and other things, like airplanes, floating or flying in the air?

Nano Scavenger Hunt
Source Institutions
This is an activity (located on page 3 of PDF under Where's Nano? Activity) about identifying nanoscale objects and phenomena in today's world.

Rolling Action Art
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners of all ages will roll a ball coated with paint to artistically visualize the motion of the object.

Pitch, Roll and Yaw: The Three Axes of Rotation
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 87 of the PDF), learners move their bodies to better understand the three axes of rotation: pitch, roll and yaw.
