Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 37

Surface Area
Source Institutions
In this demonstration, learners discover that nanoparticles behave differently, in part because they have a high surface area to volume ratio.
Charge Challenge
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how objects can have positive, negative, or neutral charges, which attract, repel and move between objects.
Electroplating
Source Institutions
In this electrochemistry activity, learners will explore two examples of electroplating.

The Electric Squeeze
Source Institutions
In this activity/demo about piezoelectricity, learners discover how some crystals produce electricity when squeezed.

Radioactive Decay of Candium
Source Institutions
In this simulation, learners use M&M™ candy to explore radioactive isotope decay.

What Shape Is It?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners determine the shape of an unseen object by bouncing a ball off the object.

Making a Battery from a Potato
Source Institutions
In this electrochemistry activity, young learners and adult helpers create a battery from a potato to run a clock.

Sweetly Balanced Equations
Source Institutions
In this (edible) activity, learners balance chemical equations using different kinds and colors of candy that represent different atoms. Learners will work in pairs and explore conservation of atoms.

Fast Rusting
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct an experiment to find out if steel wool will weigh more or less when it is burned. Learners will explore the effects of oxidation and rusting on the steel wool.

LEGO® Chemical Reactions
Source Institutions
This activity uses LEGO® bricks to represent atoms bonding into molecules and crystals. The lesson plan is for a 2.5 hour workshop (or four 45-minute classes).

Pea Brain!: Explorations in Estimation
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use two different techniques to estimate how many little things fit into one bigger thing.

Size and Scale: Probing and Predicting
Source Institutions
In this quick activity about predicting (located on page 2 of the PDF under Where's Nano?
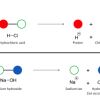
Chemical Identification
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover how a cabbage juice indicator helps identify acids and bases, and how iodine indicates the presence of starch.
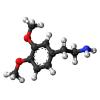
Ionic Bonding Puzzle Lab
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create models of ionic compounds and observe the chemical formula of binary molecules they have created.

How Small Can You Cut?
Source Institutions
In this lesson, learners cut paper into very small pieces to explore the small size of quarks, the smallest thing we know of on Earth.

Molecular Menagerie
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use molecular model kits to construct familiar molecules like lactose, caffeine, and Aspirin.

Toast a Mole!
Source Institutions
In this quick activity, learners drink Avogadro's number worth of molecules - 6.02x10^23 molecules!

Copper Caper
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct an oxidation experiment that turns old pennies bright and shiny. Learners soak 20 dull, dirty pennies in a bowl of salt and vinegar for five minutes.
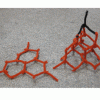
Carbon Configurations
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use geometry to predict the shape of carbon. Learners twist and attach chenille stem pieces that represent bonds between different carbon atoms.

Mixtures and Solutions
Source Institutions
This activity was designed for blind learners, but all types of learners can use it to investigate heterogeneous and homogeneous mixtures and solutions, identify the differences, and explore the conce
