Search Results
Showing results 21 to 40 of 46

Jumpin' the Gap
Source Institutions
In this simulation of synapses, learners act out communication at the neural level by behaving as pre-synaptic vesicles, neurotransmitters, post-synaptic receptors, secondary messengers and re-uptake
Bending Light
Source Institutions
In this optics activity, learners make a lens and explore how the eye manipulates the light that enters it.

Keep a "SLOG" (Sleep Log)
Source Institutions
In this activity (1st on the page), learners keep a "SLOG" or Sleep Log to study their sleep patterns.
Build-A-Membrane
Source Institutions
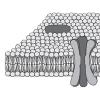
In this activity, learners cut, fold, and paste paper representing biomolecules to create a three-dimensional cell membrane with embedded proteins.

Color Code
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct the "Stroop Effect" test and explore what happens when they try to complete two simple tasks at the same time.

Tactile Double Trouble
Source Institutions
In this activity (11th activity on the page), learners use their sense of touch to identify matching pairs of objects hidden in bags. Learners can also play this game with partners.

Cover Up!
Source Institutions
Learners test their memory and ability to learn memory strategies in this game. Partners start with an array of poker chips, coins, or paper squares on the table.

Color Spy
Source Institutions
In this activity (16th on the page), learners play a variation of the "I Spy" game to explore color. Learners work in teams with each team assigned a color.

X-Ray Vision?
Source Institutions
In this activity (13th on the page), learners complete a simple illusion trick to see through their own hand.

Phenakistascope
Source Institutions
In this optics activity, learners build an animation tool to make mini movies. When you spin a phenakistascope, the pictures move so quickly that your eyes and brain can't separate the images.
Throw Your Weight Around
Source Institutions
During this activity, learners take part in a variety of tasks which involve moving and balancing different body parts.

Brain Box (Bag) of Science
Source Institutions
In this neuroscience activity (5th activity on the page), learners explore their sense of touch without using their senses of vision and hearing.
Train Your Brain
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners play a trick on their own brain to see if the brain can learn to ignore distracting input. Colors and words are used to play the visual trick, known as a Stroop Test.

Right Eye/Left Eye
Source Institutions
In this activity (3rd on the page), learners conduct a series of tests to find out which of their eyes is more dominant.

Tactile Mazes
Source Institutions
In this activity (15th activity on the page) about the sense of touch, learners use glue and cardboard to construct a maze they use with their eyes closed.
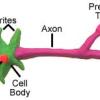
The Model Neuron
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create a model of a neuron by using colored clay or play dough. Learners use diagrams to build the model and then label the parts on a piece of paper.

Lateral Inhibition
Source Institutions
Which one of your eyes are dominant? Do they act independently or are they equally "in control?" This activity explores how your eyes work (or don't work) together.

Two Ears are Better Than One: Sound Localization
Source Institutions
This activity (9th activity on the page) about hearing demonstrates to learners the importance of having two ears.
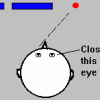
The Blind Spot
Source Institutions
In this activity (1st on the page), learners find their blind spot--the area on the retina without receptors that respond to light.

See It to Believe It: Visual Discrimination
Source Institutions
In this activity (12th on the page), learners investigate their ability to discriminate (see) different colors.
