Search Results
Showing results 21 to 39 of 39

What's That Sound?
Source Institutions
This game plays a dozen different sounds, altered to simulate what they would sound like if you had hearing loss.

Musical Coat Hangers
Source Institutions
Discover how sound travels and what materials make better sound conductors. Can you hear better with your fingers in your ears? Find out with a coat hanger and some string!

Auditory Acuity
Source Institutions
This activity (8th activity on the page) tests learners' ability to identify things using only the sense of hearing.

Stereo Hanger
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate sound wave science, in stereo! Learners construct a "stereo" out of a metal coat hanger and piece of string to explore sound vibrations.

Build a Soundscape
Source Institutions
This is a virtual representation of a sound mixer containing pre-looped sounds of animal, insect, and environmental noises.

Two Ears are Better Than One: Sound Localization
Source Institutions
This activity (9th activity on the page) about hearing demonstrates to learners the importance of having two ears.

Silent Stalking
Source Institutions
In this outdoor game, learners role play predator and prey to explore the importance of keen hearing and silent stalking skills in the animal world.
Bend It, Break It
Source Institutions
In this activity (on pages 25-32 of PDF), learners make models of the inner ear out of pipe cleaners.

Our Sense of Hearing
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate the sense of hearing and plan and conduct their own experiments.

Mystery Noises
Source Institutions
In this game (4th activity on the page) about hearing, learners test their ability to identify various sounds without looking.

How Loud is Too Loud
Source Institutions
In this activity (described on pages 39-42 of PDF), learners make a paper wheel (on pages 57-60 of PDF) that shows them the relative loudness of different sounds.

Right Ear/Left Ear
Source Institutions
In this activity (4th on the page), learners conduct a series of tests to find out which of their ears is more dominant.

Hilarious Honker
Source Institutions
Make a hilarious honker! Fasten a piece of string through a hole in the end of a plastic cup and discover the hilarious sounds you can make.

String Thing
Source Institutions
String Thing is an interactive online game in which learners change a virtual string's tension, length, and gauge to create different musical pitches.
Good Vibrations
Source Institutions
This lesson (on pages 15-24 of PDF) explores how sound is caused by vibrating objects. It explains that we hear by feeling vibrations passing through the air.

A Penny Saved is a Penny Heard
Source Institutions
In this activity (11th activity on the page), learners use pennies to test their hearing acuity.
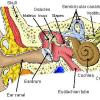
Model Eardrum
Source Institutions
In this activity (last activity on the page), learners make a model of the eardrum (also called the "tympanic membrane") and see how sound travels through the air.

Headphone Helper
Source Institutions
In this design challenge activity, learners add headphones to a previously built instrument (see "Build a Band" activity) to make it easier to hear.

Sound Off!
Source Institutions
This activity includes several games about animal sounds. Using their sense of hearing and communicating with various kinds of noisemakers, learners role-play predator and prey.
