Search Results
Showing results 621 to 640 of 1185

The Power of Graphene
Source Institutions
This lesson focuses on graphene and its electrical properties and applications.

Fungus Among Us
Source Institutions
In this environmental health activity, learners grow and observe bread mold and other kinds of common fungi over the course of 3-7 days.

DIY Science: Water Cycle in a Bag!
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners will simulate the processes of the water cycle at home in a plastic sandwich bag.

Marine Ecosystems
Source Institutions
In the wild, small crustaceans known as brine shrimp live in marine habitats such as saltwater lakes.
Water Treatment
Source Institutions
Water treatment on a large scale enables the supply of clean drinking water to communities.
Water Motor
Source Institutions
In this physics activity (page 10 of the PDF), learners will explore how energy from moving water can be used.
Flubber
Source Institutions
Learners experiment with a piece of Silly Putty® by stretching, bouncing, and snapping it. They then create flubber, a similar substance, by mixing diluted glue and a solution of sodium borate.

Bubble Bomb
Source Institutions
Learn about chemical reactions by making a Bubble Bomb, a plastic bag you can pop with the power of fizz.

Animal Reflection Response
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 1 of the PDF under SciGirls Activity: Horse Ears), learners observe how an animal responds to its own reflection.

Sweat Spot
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use a chemical reaction to visualize where moisture forms on the body.
Globby Gooey Gak
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners concoct some stretchy green goo called Gak. This activity will introduce learners to polymers, chemical reactions, and how scientists invent new materials.
Sock Garden
Source Institutions
In this activity (located in the middle of the page), learners start a garden by planting their socks!
Dispersing Dispersion
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate the movement caused by dispersion. Learners discover that dispersion is the random movement of objects.

Size, Mass, Area, and Volume
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 23 of PDF), learners conduct an experiment to determine how the size and mass of a projectile affects the area and the volume of an impact crater.

Echolocation Lab
Source Institutions
In this lab, learners experience how dolphins and other echolocating animals use their senses to locate and identify objects without using their sense of sight.
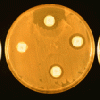
Chemical Methods of Control
Source Institutions
In this lab, learners evaluate the relative effectiveness of various chemical substances (i.e. garlic powder, bathroom cleaner, mouthwash, etc.) as antimicrobial agents.

Runaway Runoff
Source Institutions
When it rains, water can collect on top of and seep into the ground. Water can also run downhill, carrying soil and pollution with it.

Dissolving a Substance in Different Liquids
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make colored sugar and add it to water, alcohol, and oil to discover some interesting differences in dissolving.

Candy Chemistry
Source Institutions
In this experiment, learners test multiple food items to see if they are an acid or base using an indicator solution created with red cabbage.

