Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 50

Lean, Mean Information Machine: Using a Simple Model to Learn about Chromosomal DNA
Source Institutions
Learners observe a model of a cell and its chromosomal DNA made from a plastic egg and dental floss. Use this model to illustrate how much DNA is held in one cell.

How Do Viruses Recognize a Target Cell?
Source Institutions
This activity demonstrates the specificity of viral vectors for target cells in gene therapy delivery methods using two approaches: 1) STYROFOAM® models demonstrate viral ligand binding to receptor pr
String Genome
Source Institutions
In this biology activity (page 5 of the PDF), learners use yarn and sticky labels to build a model of a DNA strand. They discover that DNA is very long, very skinny, and packs well into cells.

Cells and Walls
Source Institutions
Using toothpicks, straws, or tubes of rolled up newspaper, learners create 3-dimensional models to illustrate the basic structure and function of the cell membrane, and place an object inside to repre
Modeling Limits to Cell Size
Source Institutions
This investigation provides learners with a hands-on activity that simulates the changing relationship of surface areas-to-volume for a growing cell.
Inside DNA
Source Institutions
In this activity (on pages 34-39), learners make a fairly detailed model of DNA using licorice and gumdrops.
Visualizing How the Vestibular System Works
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 59 of the PDF), learners spin and observe false eyelashes in jars of water (prepared at least 1 day ahead of time) to investigate the effects of different types of motion on the

Make a "Mummy"
Source Institutions
The Ancient Egyptians used a naturally-occurring salt from the banks of the Nile River, called natron, to mummify their dead.

Make a Heart Valve
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make a model of a one-way heart valve to investigate how a heart controls the direction of blood flow.
Building a 3-D Space Maze: Escher Staircase
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 95 of the PDF), learners create Escher Staircase models similar to those that were used by Neurolab's Spatial Orientation Team to investigate the processing of information about
Pathways with Friends
Source Institutions
Directed by instructional cards, learners kinesthetically model cell communication by acting as components in a cell signaling pathway.
Modeling an HIV Particle
Source Institutions
This activity helps learners visualize the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) by constructing three-dimensional HIV particle models from paper.

Pitch, Roll and Yaw: The Three Axes of Rotation
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 87 of the PDF), learners move their bodies to better understand the three axes of rotation: pitch, roll and yaw.

Breakfast Proteins
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners construct a cereal chain as a model of how proteins are made in the cell.

Chromosome Models: Karyotyping
Source Institutions
This activity was designed for blind learners, but all types of learners can have a tactile opportunity to construct a karyotype, an organized model of an organism’s chromosomes, conveying the chromos

Human Impact on Estuaries: A Terrible Spill in Grand Bay
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make a model of a pollution spill that occurred at Bangs Lake in Mississippi and measure water quality parameters in their model.

Glitter Slime
Source Institutions
Our bodies defend themselves in many different ways to prevent us from getting sick.

Molecular Menagerie
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use molecular model kits to construct familiar molecules like lactose, caffeine, and Aspirin.
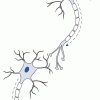
What Is a Neuron?
Source Institutions
This neuroscience activity introduces learners to how messages are sent and received by neurons. Learners use modeling clay and pipe cleaners to build model neurons.

Biobarcodes: Antibodies and Nanosensors
Source Institutions
In this activity/demo, learners investigate biobarcodes, a nanomedical technology that allows for massively parallel testing that can assist with disease diagnosis.
