Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 62
Mercury in the Environment
Source Institutions
In this environmental science lesson, learners will examine the dangers of mercury and how humans contribute to growing mercury emissions on Earth.
Trading Places: Redox Reactions
Source Institutions
Visitors add drops of copper sulfate solution onto a steel nail. They observe the nail change color from silver to brown as the copper plates onto the nail.
Currently Working: Testing Conductivity
Source Institutions
Visitors test solutions of water, sugar, salt, and hydrochloric acid and the solids salt and sugar. They clip leads from the hand generator to wires immersed in each substance.
Forwards and Backwards: pH and Indicators
Source Institutions
Visitors prepare six solutions combining vinegar and ammonia that range incrementally from acid (all vinegar) to base (all ammonia).
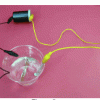
Electroplating
Source Institutions
In this electrochemistry activity, learners will explore two examples of electroplating.

Making a Battery from a Potato
Source Institutions
In this electrochemistry activity, young learners and adult helpers create a battery from a potato to run a clock.

Oil Spill Cleanup
This hands-on experiment will provide learners with an understanding of the issues that surround environmental cleanup.
Light and Sound
Source Institutions
In this four-part activity, learners explore light and sound through a variety of hands-on investigations.
Hot and Cold: Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions
Source Institutions
Visitors mix urea with water in one flask and mix calcium chloride with water in another flask. They observe that the urea flask gets cold and the calcium chloride flask gets hot.
Yeast Balloons
Source Institutions
Visitors observe a bottle with a balloon attached around the mouth. The bottle contains a solution of yeast, sugar, and water.

3-2-1 POP!
Source Institutions
In this physics activity, learners build their own rockets out of film canisters and construction paper.
It's A Gas!
Source Institutions
Visitors mix water and sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) in a large flask. They then add citric acid to the mixture and stopper the flask. The resulting reaction creates carbon dioxide gas.
All Mixed Up!: Separating Mixtures
Source Institutions
Visitors separate a mixture of pebbles, salt crystals, and wood shavings by adding water and pouring the mixture through a strainer.
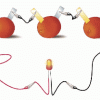
Electricity: Fruit Batteries
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create a battery from fruit. This activity helps learners explore electricity, electrochemistry, and series circuits as well as the process of scientific inquiry.
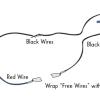
Neural Network Signals
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create an electrical circuit and investigate how some dissolved substances conduct electricity.

Fuel for Living Things
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners observe what happens when yeast cells are provided with a source of food (sugar). Red cabbage "juice" will serve as an indicator for the presence of carbon dioxide.
What Does Life Need to Live?
Source Institutions
In this astrobiology activity (on page 11 of the PDF), learners consider what organisms need in order to live (water, nutrients, and energy).

Luminescence
Source Institutions
In this two-part activity about luminescence, learners explore the chemistry that happens inside glow sticks and other light producing reactions.

The Carbon Cycle: How It Works
Source Institutions
In this game, learners walk through an imaginary Carbon Cycle and explore the ways in which carbon is stored in reservoirs and the processes that transport the carbon atom from one location to another
Rain Machine (Solar Still)
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners work in groups to build simple solar stills filled with salt water. After the stills are complete, learners observe what happens when they place the stills in the sun.
