Search Results
Showing results 141 to 160 of 644

Indicating Electrolysis
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build a simple electrolysis device. Then learners use an indicating solution to visualize hydrogen and oxygen molecules in water.

Introduction to the Scientific Method
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 26 of the PDF), learners make observations, formulate hypotheses and design a controlled experiment, based on the reaction of carbon dioxide with calcium hydroxide.

Hot Stuff!: Testing for Carbon Dioxide from Our Own Breath
Learners blow into balloons and collect their breath--carbon dioxide gas (CO2). They then blow the CO2 from the balloon into a solution of acid-base indicator.
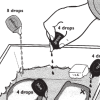
Spill Spread
Source Institutions
In this simulation, learners explore how ocean currents spread all kinds of pollution—including oil spills, sewage, pesticides and factory waste—far beyond where the pollution originates.
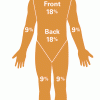
Measuring and Protecting Skin
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners compare and contrast their own skin (including the area covered) with that of an orange.

Portable Sundial
Source Institutions
Learners construct one or more of the following kinds of sundials: a shadow plot, a horizontal sundial, and a diptych sundial.
Earth Attractions
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build and test a compass. Learners work in pairs and pretend they are stuck in the wilderness at night.

Kites
Source Institutions
In this engineering/design activity, learners make a kite, fly it, and then work to improve the design. Learners explore how their kite design variations affect flight.

A Merry-Go-Round for Dirty Air
Learners build a model of a pollution control device--a cyclone. A cyclone works by whirling the polluted air in a circle and accumulating particles on the edges of the container.
Making Regolith
Source Institutions
This lesson will helps learners answer the question: How does the bombardment of micrometeoroids make regolith on the moon?

Water Underground
Source Institutions
Many people get water from a source deep underground, called groundwater.

Erosion
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners model erosion using a clear shoebox and sand or soil.

The Great Plankton Race
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners are challenged to design a planktonic organism that will neither float like a cork nor sink like a stone.
How Does Water Climb a Tree?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct an experiment to explore how water flows up from a tree's roots to its leafy crown.

Exploring the Solar System: Stomp Rockets
Source Institutions
In "Exploring the Solar System: Stomp Rockets," participants learn about how some rockets carry science tools—not scientists—into space, and how a special kind of rocket called "sounding rockets" can

Water: Clearly Unique!
Source Institutions
In this activity on page 4 of the PDF (Water in Our World), learners conduct some quick and easy tests to determine the differences between water and other liquids that look very similar to water.

Destination Tidepool
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 7 of pdf), learners research tide pool ecosystems, and then create brochures that "advertise" these environments.

Model the Sun and Earth
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make scale models of the Sun and Earth out of paper mache.

Collect Invertebrates to Determine Water Quality
Source Institutions
This activity (located on page 3 of the PDF under GPS: Alligator Habitat Activity) is a full inquiry investigation into organisms and the health of their ecosystems.

What's in the Water?: Biotic and Abiotic Elements in Aquatic Ecosystems
Source Institutions
In this investigation learners explore the differences between, and interdependence of, living and nonliving elements in a water ecosystem.
