Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 34

Protect That BRAIN!: Mr. Egghead
Source Institutions
This activity demonstrates the importance of wearing a helmet to protect the brain. An egg is used to symbolize a head with the shell as the skull and the inside of the egg as the brain.

Brain Box (Bag) of Science
Source Institutions
In this neuroscience activity (5th activity on the page), learners explore their sense of touch without using their senses of vision and hearing.

Color Code
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct the "Stroop Effect" test and explore what happens when they try to complete two simple tasks at the same time.

Drugs, Risks and the Nervous System
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners estimate risks associated with different events and compare their estimates to the real possibilities.
Building a Magic Carpet
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 89 of the PDF), learners compare and contrast pitch and roll motions by using a Magic Carpet maze similar to one that was used for Neurolab investigations about microgravity.

Measuring Your Breathing Frequency at Rest
Source Institutions
In this activity about the brain and sleep (on page 138 of the PDF), learners measure their resting breathing rates. Learners will discover that breathing frequencies vary amongst individuals.
Building a 3-D Space Maze: Escher Staircase
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 95 of the PDF), learners create Escher Staircase models similar to those that were used by Neurolab's Spatial Orientation Team to investigate the processing of information about

Changing Body Positions: How Does the Circulatory System Adjust?
Source Institutions
In this activity about how the body regulates blood pressure (page 117 of the PDF), learners make and compare measurements of heart rate and blood pressure from three body positions: sitting, standing

Blind Spot
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct a simple test to find their blind spot.
Expose Your Nose
Source Institutions
In this simple exploratory activity (1st activity on the page), blindfolded learners try to identify mystery items by smell.
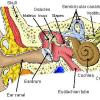
Model Eardrum
Source Institutions
In this activity (last activity on the page), learners make a model of the eardrum (also called the "tympanic membrane") and see how sound travels through the air.

X-Ray Vision?
Source Institutions
In this activity (13th on the page), learners complete a simple illusion trick to see through their own hand.
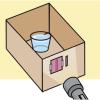
Bending Light
Source Institutions
In this optics activity, learners make a lens and explore how the eye manipulates the light that enters it.

Keep a "SLOG" (Sleep Log)
Source Institutions
In this activity (1st on the page), learners keep a "SLOG" or Sleep Log to study their sleep patterns.

Two Ears are Better Than One: Sound Localization
Source Institutions
This activity (9th activity on the page) about hearing demonstrates to learners the importance of having two ears.
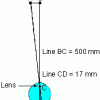
Measuring Your Blind Spot
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners calculate the width (horizontal diameter) of the blind spot on their retina. Learners make a blind spot tester using a piece of notebook paper.
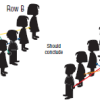
Target Recognition and Synapse Formation During Development
Source Institutions
In this activity about neuron/target muscle recognition (page 44 of the PDF), learners arranged in two rows facing away from each other use string to simulate neural development.

Right Eye/Left Eye
Source Institutions
In this activity (3rd on the page), learners conduct a series of tests to find out which of their eyes is more dominant.
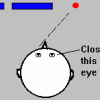
The Blind Spot
Source Institutions
In this activity (1st on the page), learners find their blind spot--the area on the retina without receptors that respond to light.

See It to Believe It: Visual Discrimination
Source Institutions
In this activity (12th on the page), learners investigate their ability to discriminate (see) different colors.
