Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 21

Programming Languages: Marching Orders
Source Institutions
In this activity about computer programming, learners follow instructions in a variety of ways in order to successfully draw figures.
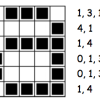
Colour by Numbers: Image Representation
Source Institutions
This activity shows learners how computers use numbers to represent pictures. A grid is used to represent the pixels (short for picture elements) of a computer screen.

Battleships: Searching Algorithms
Source Institutions
This activity explores the main algorithms that are used as the basis for searching on computers, using different variations on the game of battleships.

The Muddy City: Minimal Spanning Trees
Source Institutions
In this puzzle, learners investigate the decisions involved in linking a network between houses in a muddy city.
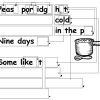
You Can Say That Again!: Text Compression
Source Institutions
This activity helps students learn how computers "compress" text by identifying repeating patterns of letters, words, and phrases.

The Poor Cartographer: Graph Coloring
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners help a poor cartographer color in the countries on a map, making sure each country is colored a different color than any of its neighbors.

Card Flip Magic: Error Detection & Correction
Source Institutions
This magic trick is based on how computers detect and correct data errors.
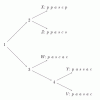
Phylogenetics
Source Institutions
This activity lets learners participate in the process of reconstructing a phylogenetic tree and introduces them to several core bioinformatics concepts, particularly in relation to evolution.
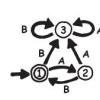
Treasure Hunt: Finite-State Automata
In this computer science activity about finite-state automaton (on page 45 of the PDF), learners use a map and choose various pathways to find Treasure Island.
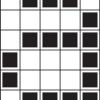
Color by Numbers: Image Representation
Source Institutions
Computers store drawings, photographs, and other pictures using only numbers. Through this activity, learners decode numbers to create pictures using the same process that computers use.

Program a Friend
Source Institutions
In this activity (on page 2), one person "programs" the other like a robot to move through a space, trying to get them to avoid obstacles and reach a goal.
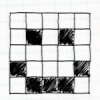
Passion for Pixels
Source Institutions
In this technology activity, learners explore digital imaging and pixels. Learners "transmit" an image to a partner by creating an image on grid paper.

The Orange Game: Routing and Deadlock in Networks
Source Institutions
When a lot of people share one network (such as cars using roads, or messages getting through the Internet), there is the possibility that competing processes will create a “deadlock," or an interrupt
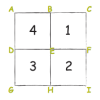
Solving Playground Network Problems
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use cooperation and logical thinking to find solutions to network problems on the playground.

Binary Code Bracelets
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make their own binary code bracelets by translating their initials into 0s and 1s represented by beads of 2 different colors.
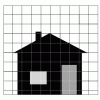
Paint by the Numbers
Source Institutions
In this pencil and paper activity, learners work in pairs and simulate how astronomical spacecraft and computers create images of objects in space.
Measurement: It Takes Ten
Source Institutions
In this math lesson, learners practice estimation and measurement skills as they move from station to station calculating length, volume, weight, and area.
Tic-Tac-Toe
Source Institutions
In this online version of the classic paper and pencil game, learners practice looking ahead to anticipate an opponent's move.
Geometry and Spatial Relations: Mirror, Mirror
Source Institutions
In this math lesson, learners use hinged mirrors to discover that regular polygons are composed of triangles tessellating around a center point.

Baseball
Source Institutions
In this math activity (Page 17 of the Play Ball! PDF), learners play a game of "baseball" and analyze the results of the game.
