Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 27

How Sweet It Is
Source Institutions
In this activity (4th activity on the page), learners use their sense of smell to rate and arrange containers filled with different dilutions of a scent (like cologne or fruit juice) in order from wea

Radar Mapping: What's in the Box?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners mimic remote sensing. Learners use a stick to measure the distance to a "planet surface" they cannot see, and create their own map of the landscape.

The Senses of "Unknown Creatures"
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use earthworms as "unknown creatures" from the South American jungle to find out how animals use senses.

Echolocation Lab
Source Institutions
In this lab, learners experience how dolphins and other echolocating animals use their senses to locate and identify objects without using their sense of sight.

Auditory Acuity
Source Institutions
This activity (8th activity on the page) tests learners' ability to identify things using only the sense of hearing.

Make a Comet Model and Eat It!
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build models of comets, using edible materials, to learn about comets' structure.
Sensory Hi-Lo Hunt
Source Institutions
In this outdoor activity, learners use only their senses to to find the extremes of several environmental variables or physical factors: wind, temperature, light, slope and moisture.
Our Sense of Sight: Eye Anatomy and Function
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate the sense of sight and develop and conduct their own experiments.

Our Sense of Hearing
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate the sense of hearing and plan and conduct their own experiments.
Exploring Liquids
Source Institutions
Young learners investigate and observe the properties of three liquids -- water, vegetable oil, and corn syrup. They use their senses to collect data and ask and answer questions.
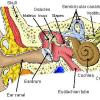
Model Eardrum
Source Institutions
In this activity (last activity on the page), learners make a model of the eardrum (also called the "tympanic membrane") and see how sound travels through the air.

Two Ears are Better Than One: Sound Localization
Source Institutions
This activity (9th activity on the page) about hearing demonstrates to learners the importance of having two ears.

No Saliva, No Taste?
Source Institutions
In this activity (4th activity on the page), learners test to see if saliva is necessary for food to have taste.
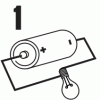
Circuit Sense
Source Institutions
In this activity about electricity, learners identify closed and open circuits. First, learners examine and label diagrams of open and closed circuits.
Finding the Size of the Sun and Moon
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners build a simple pinhole viewer. They use this apparatus to project images from a variety of light sources, including a candle, the Sun, and the Moon.

Changing Shadows
Source Institutions
In this sunny day, outdoor activity, learners observe changes in shadows over time. The activity also helps to develop a sense of the Earth's motion.

A Penny Saved is a Penny Heard
Source Institutions
In this activity (11th activity on the page), learners use pennies to test their hearing acuity.

New Sense about Cents
Source Institutions
In this activity on page 6 of the PDF (Chemistry—It’s Elemental), learners explore some of the properties of copper using a few common household ingredients.

Exploring Size: Scented Solutions
Source Institutions
This is an activity in which learners will find that they can detect differences in concentration better with their nose (smelling) than with their eyes (seeing).

Half Full or Half Empty
Source Institutions
In this activity (12th activity on the page), learners conduct an experiment to demonstrate how muscles are constantly feeding information to the brain about what they are doing.
