Search Results
Showing results 1 to 20 of 23
Charge Challenge
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore how objects can have positive, negative, or neutral charges, which attract, repel and move between objects.
Electroplating
Source Institutions
In this electrochemistry activity, learners will explore two examples of electroplating.

Radioactive Decay of Candium
Source Institutions
In this simulation, learners use M&M™ candy to explore radioactive isotope decay.

What Shape Is It?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners determine the shape of an unseen object by bouncing a ball off the object.

Making a Battery from a Potato
Source Institutions
In this electrochemistry activity, young learners and adult helpers create a battery from a potato to run a clock.

Fast Rusting
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct an experiment to find out if steel wool will weigh more or less when it is burned. Learners will explore the effects of oxidation and rusting on the steel wool.

LEGO® Chemical Reactions
Source Institutions
This activity uses LEGO® bricks to represent atoms bonding into molecules and crystals. The lesson plan is for a 2.5 hour workshop (or four 45-minute classes).

Pea Brain!: Explorations in Estimation
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use two different techniques to estimate how many little things fit into one bigger thing.

Size and Scale: Probing and Predicting
Source Institutions
In this quick activity about predicting (located on page 2 of the PDF under Where's Nano?
Chemical Identification
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners discover how a cabbage juice indicator helps identify acids and bases, and how iodine indicates the presence of starch.
Ionic Bonding Puzzle Lab
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create models of ionic compounds and observe the chemical formula of binary molecules they have created.

How Small Can You Cut?
Source Institutions
In this lesson, learners cut paper into very small pieces to explore the small size of quarks, the smallest thing we know of on Earth.

Copper Caper
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners conduct an oxidation experiment that turns old pennies bright and shiny. Learners soak 20 dull, dirty pennies in a bowl of salt and vinegar for five minutes.
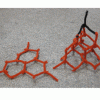
Carbon Configurations
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use geometry to predict the shape of carbon. Learners twist and attach chenille stem pieces that represent bonds between different carbon atoms.
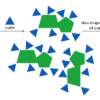
Chemistry in the Kitchen
Source Institutions
In this kitchen chemistry activity, learners explore the chemistry of crystals by making sugar crystals, consider a common chemical reaction type responsible for the rising of muffins and cake in the

Curie Point
Source Institutions
In this activity best suited as a demonstration, learners observe that when a piece of iron gets too hot, it loses its ability to be magnetized.

Below the Surface: Surface Tension II
Source Institutions
In this activity learners explore surface tension. Why are certain objects able to float on the surface of water and how do detergents break the surface tension of water?
Gas Model
Source Institutions
This highly visual model demonstrates the atomic theory of matter which states that a gas is made up of tiny particles of atoms that are in constant motion, smashing into each other.

Radioactive-Decay Model: Substitute coins for radiation
Source Institutions
Get a roll of pennies, throw them on the ground, then remove those that only show tails, and repeat with the ones left over.

Big Things Come in Little Packages
Source Institutions
As a group, learners investigate three packages which are all the same size and shape, but have different contents. One is filled with foam, one is filled with wood, and one is filled with metal.
