Search Results
Showing results 21 to 40 of 48
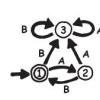
Treasure Hunt: Finite-State Automata
In this computer science activity about finite-state automaton (on page 45 of the PDF), learners use a map and choose various pathways to find Treasure Island.

Beat the Clock: Sorting Networks
Source Institutions
Even fast computers are limited to how quickly they can solve problems. One way to speed things up is to use several computers at once.

EEEEK--A Mouse!
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore the concept of how engineering solved the problem of human/computer interface.
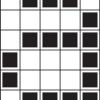
Color by Numbers: Image Representation
Source Institutions
Computers store drawings, photographs, and other pictures using only numbers. Through this activity, learners decode numbers to create pictures using the same process that computers use.

Count the Dots: Binary Numbers
Source Institutions
Data in computers is stored and transmitted as a series of zeros and ones. Learners explore how to represent numbers using just these two symbols, through a binary system of cards.

Program a Friend
Source Institutions
In this activity (on page 2), one person "programs" the other like a robot to move through a space, trying to get them to avoid obstacles and reach a goal.

Pico Cricket Compass
Source Institutions
Learners can program a compass to draw a circle by itself using a Pico Cricket, some Legos, and lots of tape! Pico Cricket is required.

Patterns in Pixels
Source Institutions
This activity (page 2) draws upon a familiar, computer-based concept related to visual resolution: pixilation.

Cipher Wheel
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make their own encrypted code to pass along secret messages using a printable cipher wheel.

What am I?
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners examine nanoscale structures of common things.
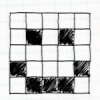
Passion for Pixels
Source Institutions
In this technology activity, learners explore digital imaging and pixels. Learners "transmit" an image to a partner by creating an image on grid paper.
Lightest and Heaviest: Sorting Algorithms
Source Institutions
Computers are often used to put lists into some sort of order—for example, names into alphabetical order, appointments or e-mail by date, or items in numerical order.

The Orange Game: Routing and Deadlock in Networks
Source Institutions
When a lot of people share one network (such as cars using roads, or messages getting through the Internet), there is the possibility that competing processes will create a “deadlock," or an interrupt
Solving Playground Network Problems
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners use cooperation and logical thinking to find solutions to network problems on the playground.

Binary Code Bracelets
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners make their own binary code bracelets by translating their initials into 0s and 1s represented by beads of 2 different colors.
Paint by the Numbers
Source Institutions
In this pencil and paper activity, learners work in pairs and simulate how astronomical spacecraft and computers create images of objects in space.

LEGO Orrery
Source Institutions
Use this model to demonstrate the goal of NASA's Kepler Mission: to find extrasolar planets through the transit method.

Fruity-Glows: Pictures of Health on a Microarray Canvas
Source Institutions
In this activity (page 12), learners apply the concepts of pixilation and pointillism to the world of biomedical science.
Forward Thinking
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners create their own weather forecast map.

LEGO Robots
Source Institutions
This activity (on page 2 of the PDF under GEMS Activity) is a full inquiry investigation into technology design and testing.
