Search Results
Showing results 141 to 160 of 504

Fuel for Living Things
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners observe what happens when yeast cells are provided with a source of food (sugar). Red cabbage "juice" will serve as an indicator for the presence of carbon dioxide.

Lilliputian Landscaping
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners examine the different materials gardeners add to their soil, and discuss how these materials are important for plant growth.
DNA Extraction: Look at your genes!
Source Institutions
Extract your DNA from your very own cells! First, learners swish salt water in their mouth to collect cheek cells and spit the water into a glass.

Wheat Evolution: Dough Washing
Source Institutions
In this activity (Page 22 of PDF), learners investigate the evolution of wheat by washing different types of dough with water and comparing the results.

Biochemistry Happens Inside of You!
Source Institutions
In this four-part activity, learners explore how the body works and the chemistry that happens inside living things.
Our Sense of Sight: How We Perceive Movement, Depth and Illusions
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners investigate visual perception as well as plan and conduct their own experiments.

We all Scream for Ice Cream
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners observe how salinity affects the freezing point of water by making and enjoying ice cream.

Wheat Evolution: Dough Rising and Baking
Source Institutions
In this activity (Page 25 of PDF), learners investigate the evolution of wheat by creating dough from different flours, observing the samples of dough as they rise, and then baking the dough.

Rubber Bones
Source Institutions
Over 1 or 2 days, learners use vinegar to remove the calcium from a chicken bone. They then explore how the bones have changed. An accompanying video with Mr.

On the Microbe Trail: An Introduction to Bacteria and Aseptic Technique
Source Institutions
In this series of exercises, learners predict the conditions necessary for bacterial growth, test their predictions and at the same time practice the aseptic techniques and safety procedures needed wh
What Does Life Need to Live?
Source Institutions
In this astrobiology activity (on page 11 of the PDF), learners consider what organisms need in order to live (water, nutrients, and energy).
No bones about it!
Source Institutions
This is an activity (located on page 3 of the PDF) about the mixture of materials in bone and how they affect its strength.
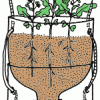
TerrAqua Investigation Column: What is the Land-Water Connection?
Source Institutions
In this investigation, learners plant seeds in a 2-liter bottle filled with soil that is connected to a water source below. Over the next few weeks, learners observe how the plants grow.
How Do Antacids Work?
Source Institutions
You just ate a big meal and feel heartburn coming on. You take an antacid and feel better. Why? Heartburn is caused by stomach juice (an acid) burning the esophagus.

Stepping Out: Hop, Skip, Jump
Source Institutions
In this activity, learners explore and experiment how we can use our bodies everyday to get from one place to another.
What's the Angle?
Source Institutions
This activity helps learners understand how the angle of the Sun affects temperatures around the globe.

Dinosaur Breath
Through discussion and hands-on experimentation, learners examine the geological (ancient) carbon cycle.

How Long Can You Hold Your Breath?
Source Institutions
In this activity (on page 142 of the PDF), learners will compare breathing rates before and after hyperventilation to explore how reduced carbon dioxide levels in the blood lower the need to breathe.
Of Cabbages and Kings
Source Institutions
This lesson gives full instructions for making cabbage juice indicator, a procedure sheet for learners to record observations as they use the indicator to test materials, and extension activities to d

How Fast Can a Carrot Rot?
Source Institutions
Learners design their own experiment to determine conditions that either help or hinder the decomposition of carrots by soil microbes.
